Recently, a screwdriver has become a fairly popular tool. For convenience, many seek to purchase a cordless screwdriver. Over time, of course, the question arises: how can I check the battery of a screwdriver?
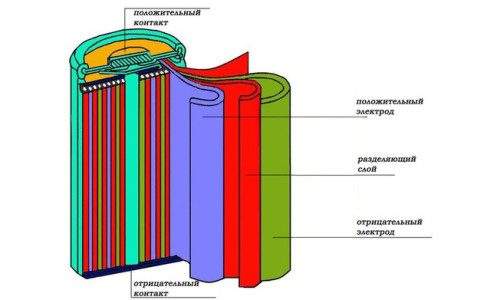
Diagram of a nickel-cadmium screwdriver battery.
The main types of batteries
The most common type of drive used in screwdrivers is a nickel-cadmium battery. The main advantages of such elements are recognized as high capacity with small dimensions and weight, as well as a sufficiently long service life (up to 3500 cycles). The electromotive force of the element reaches 1.37 V, and the specific electric energy is up to 65 Wh / kg. Limits the use of such elements (especially in imported instruments) harmful production.
Nickel-metal hydride batteries for a screwdriver are becoming the main competitor to nickel-cadmium copies. The main advantage of such elements is safety and environmental friendliness. It is recommended to store the elements in a charged state, since if they are not used for a month, they can be discharged to a state where their charging becomes impossible.
In the latest models of screwdrivers, modern promising types of batteries are used: lithium-ion and lithium-polymer. They have a very high capacity with small dimensions, but their cost is still quite large.
Battery Overview
Table of varieties of the battery.
In general, an electrical storage device is a constant current source due to the conversion of a chemical reaction into electrical energy. When working, it gives up the accumulated electricity to the electrical circuit. When charging the battery of a screwdriver, current is passed in the opposite direction and the process of energy storage proceeds.
The main parameter of any battery is the accumulated energy capacity, which indicates how much current the battery can deliver in one hour. Therefore, the battery capacity is usually measured in ampere-hours.
The principle of operation of any battery is based on electrolysis. Therefore, the battery consists of two electrodes. the anode and cathode, which are in the electrolyte. A chemical reaction causes the creation of an electric charge on the electrodes (poles). The potential difference between the electrodes determines the battery voltage, which is considered one of the most important characteristics of the battery. The series connection of individual batteries leads to the addition of their electrical voltages.
The main parameters of the drives depend on the materials of the electrodes and the composition of the electrolyte. In nickel-cadmium batteries, the anode is made from a mixture of nickel oxide hydrate and graphite, and the cathode is cadmium oxide hydrate or metallic cadmium. Potassium hydroxide with the addition of lithium hydroxide was used as an electrolyte. A similar anode is used in the nickel-metal hydride battery, but the cathode is made of an alloy of nickel with rare earth metals. In lithium-ion batteries, the cathode is made of coal, and the anode consists of lithium dioxide and cobalt. The electrolyte is a salt solution with lithium ions. The difference between the lithium-polymer variant is only a change in the composition of the electrolyte. this is a gel-like polymer substance.
Drive Verification Principles
Diagram of a device for checking batteries.
To check the battery of a screwdriver means to determine its real basic parameters. A battery check is usually carried out to determine its quality or cause of inoperability. In the first case, it is aimed at clarifying the quality of the new battery, and in the second, it includes measuring the parameters on the battery that do not feed the screwdriver in the right amount. The check is carried out only when the battery is fully charged.
When checking batteries for a screwdriver, remember the effect of the “memory effect". This phenomenon is based on the fact that frequent charging of a battery that is not fully discharged can change the capacity of the cell due to the residual charges from the previous charge. Particularly susceptible to the "memory effect" nickel-cadmium specimens. This property causes a complete “training cycle” to be carried out before the test. It consists in completely discharging the battery and then fully charging it.
The most important parameter of a screwdriver battery is its capacity. To determine it, there is a special device. a pendant type battery tester, but it is mainly used by professionals, and for most users it is not available. Therefore, this parameter is usually analyzed by evaluating other parameters. The current and voltage at the battery output are measured directly.
The first stage of verification
Checking the battery only makes sense when fully charged. The first stage of verification is carried out at the stage of charging the battery. At this stage, voltage and current are measured, as well as their recovery rate. In other words, these parameters are measured periodically after a certain period of time.
Video: How to Check Battery Capacity of a Screwdriver with a Multimeter
Battery voltage check circuit.
Voltage control is as follows. After 0.5 hours of charging, the voltage on the battery is measured. For example, it reached 13 V, which is normal. The voltage increase gradually decreases and after another 0.5 hours of charging reaches 13.5 V. The last measurement after 2 hours of charging shows a voltage of 14 V, and its growth is not observed for the last 0.5 hours. Charging has reached the maximum possible. For drives in full working condition, the voltage value is 17 V. The conclusion of such a check is that the battery has inoperative elements. In the given example, there are most likely two such elements.
The quality of the battery can also be estimated by measuring the current during charging. A normal battery is characterized by a stable increase in the typed current in the first hour of charging. If the current reaches a force above 1 A, then we can talk about the health of the battery.
If the battery is already installed in the screwdriver in a charged state (for example, a new one), then the first voltage measurement on it is performed without disassembling the tool. Using a simple tester or voltmeter, the voltage between the poles is measured. It should be remembered that the measured voltage without load corresponds to an open circuit voltage, which is slightly higher than the rated operating voltage. For example, with 12 cells at 1.2 V, each operating voltage will be 14.4 V, and the open circuit voltage is set to 17 V. If the measurement shows a voltage value lower than required, then this means that there are inoperative elements or the battery is not fully charged.
Thus, the first conclusions about battery performance can be made already at the first stage of verification, using a simple tester. Based on the results of such a check, the need for disassembling a screwdriver and a battery is established.
Load test
The circuit for checking the battery with an ammeter.
A preliminary check does not allow to evaluate the battery capacity, i.e. the time during which it will be discharged. To evaluate the parameter, it is necessary to check the battery under load. If the power is indicated on the drive, then the load power is selected by this value. If the battery power is unknown, the load can be approximately chosen on the basis that its power is half the product of the current supplied by the battery during operation and the battery voltage. Usually it is enough to use a load of 35-40 watts. As such a load, you can use a lamp for a car headlight with a power of 35 W or a spot lamp for 12 V of the same power.
A circuit is being assembled where the battery, as source of electricity, is discharged to the load through an ammeter. Voltage is measured with a voltmeter. The battery turns on for 2-3 minutes. If during this time the brightness of the load lamp has not decreased, then the battery capacity can be previously estimated as normal. This conclusion should be supported by voltage measurement (it should be more than 12.4 V). At voltages from 12 to 12.4 V, you should look for a possible damaged element. A voltage below 23 V indicates insufficient battery capacity.
If the brightness decreases markedly, then this indicates the presence of inoperative elements. And it’s really bad if the lamp goes out. This means that the battery discharges very quickly and its capacity is very small.
Checking battery cells
After a preliminary check has established the presence of malfunctions in the drive, it is necessary to open the screwdriver and remove the battery, i.e. battery cells connected in series with each other. The battery includes 10 to 12 cells (cans), each has an operating voltage of 1.2 V. Typically, a battery of 10 such cans is installed in screwdrivers.
Checking the elements begins with a visual inspection of the attachment points. Violation in the fastening (soldering, welding) can cause underestimated parameters. Then the voltage at each bank is measured. The voltage should not be less than 1.2 V. It should be borne in mind that in modern screwdriver designs heat sensors are placed to monitor battery charging. During measurements, they should be disconnected, and the device connected to the main terminals (bank poles). Identified banks with an undervalued operating voltage are disconnected from the battery and must be replaced. If a simple voltage measurement did not reveal the presence of inoperative elements, then measurements should be made under load according to a procedure similar to a preliminary test of the drive.
Resistance Check
Circuit device multimeter.
The performance of each battery jar can be more likely to be estimated by comparing the jars by their internal electrical resistance. This parameter clearly indicates battery reliability. The resistance value is determined by calculation as a result of dividing the operating voltage by the strength of the operating current minus the load resistance.
The operating voltage is necessarily measured under load, and a resistor with a precisely defined value of its own electrical resistance should be used as a load. You can recommend a resistor with a resistance of 10 ohms and a power of 25 watts to create a load. Verification is carried out for each bank separately. Measured operating voltage and current.
For example, consider the average check. For a new battery can, the internal resistance is 0.1 ohms. In general, the lower the bank’s internal resistance, the better it is. In real conditions, the operating voltage under a load of 1.19 V and the current strength of 112 mA were obtained for one can, and 1.18 V and 70 mA for the second can. The resistance is 0.63 Ohm and 5.71 Ohm, respectively.
A significant excess of resistance indicates the unsuitability of such a battery.
Checking other parameters
All batteries have a certain amount of self-discharge, i.e. discharges without load in storage conditions. So, self-discharge of nickel-cadmium batteries can reach 20% during a month of storage, nickel-metal hydride. up to 30%, lithium-ion. up to 8%. Self-discharge is recommended to be controlled by measuring the voltage every day for a month.
Checking for the presence of a “memory effect" is advisable, as it helps to eliminate its harmful effects. It is carried out by conducting several (3-4 times) cycles: full discharge-full charge of the battery. The battery can be discharged through a load, which uses a 12-volt light bulb. The residual operating voltage and open circuit voltage are measured. With such repeated trainings, the “memory effect” should disappear.
Essential tool
When checking the battery of a screwdriver, the following tools and devices are required:
- 15 V DC voltmeter;
- ammeter and milliammeter of direct current;
- tester;
- multimeter;
- pliers;
- screwdriver;
- knife;
- soldering iron.
To determine the malfunction of the battery, it is necessary to conduct a full check of its elements. Such a check can be done by any user with a screwdriver.