Wood and metal processing
In cases where the operation to separate a part of the metal from the workpiece is impossible (or impractical) to be performed by cutting, they resort to cutting.
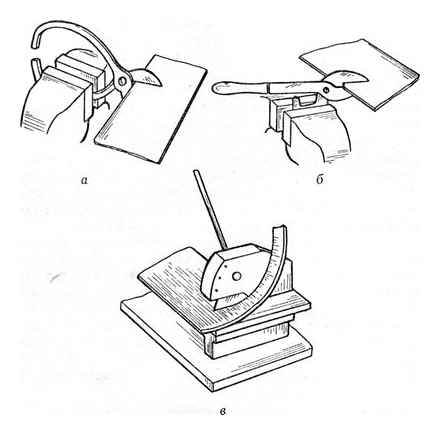
The choice of tool for this operation depends on the type of metal being processed. So, sheet metal up to 0.5 mm thick (and sheets of brass and aluminum. up to 1 mm) can be cut with hand scissors. In this case, the blades of the scissors should be diluted by about three quarters of their length, and the sheet of metal should be positioned perpendicular to the plane of the cutting edges of the scissors. When squeezing the handles of the scissors, the blades should not be fully brought together, as this leads to the metal breaking at the end of the cut. For round workpieces, it is more expedient to cut metal counterclockwise, for which the workpiece should be turned clockwise.
If the thickness of the sheet to be cut is slightly larger (up to 0.7 and 1.5 mm, respectively), then you can use the same hand scissors, but grip one of the handles in a vice, and press the other hand from above Metal with a thickness of over 0.7 mm (a brass and aluminum. over 1.5 mm) cannot be cut with ordinary hand scissors. In these cases, power scissors should be used. Fasten the handle without a plastic tip in a vise, and grip the operating handle (with a plastic tip) by hand. The cutting force due to the use of the lever increases approximately 2 times compared to conventional hand shears. The knives on the power scissors can be changed, this is provided for by their design. In addition, power shears usually have a device for cutting metal rods up to 8 mm in diameter.
If your workshop is equipped with lever scissors, you can cut sheet steel up to 4mm thick (and brass and aluminum up to 6mm thick) rather quickly (and relatively easily). Before using the lever scissors, make sure that the base of the scissors is securely attached to the table top of the locksmith’s workbench, for this they are provided with bolts. Metal cutting occurs as a result of the movement of the handle (lever), to which one of the scissors knives is attached, down.
You need to press the handle of the lever scissors smoothly, without jerking. On them (unlike manual and power ones), metal cutting is possible only along a straight mowing line.
When working with thick sheets of strip or profile metal, and also if you do not need to cut the metal, but cut a groove or slot, then a hacksaw or a jigsaw for metal (hereinafter: “hacksaw”) replaces the scissors. But before you start working with these tools, you must first configure them correctly.
First, you need to choose a hacksaw blade. It is selected depending on the type of metal.
Cutting Metal With a Hacksaw
Secondly, the blade must be properly tensioned in the hacksaw frame: the degree of tension can be easily checked by lightly pressing the blade from the side. if it does not bend, then the tension is sufficient.
The most convenient position of the hands when working with a hacksaw is as follows: the end of the handle rests against the middle of the palm of the right hand, and the fingers of the left hand grasp the tension screw of the movable head. The hacksaw should be moved smoothly, without jerks; frequency of movements. 30-60 double strokes (from oneself. to oneself) per minute; in this case, at least 2/3 of the blade length should work. The hacksaw blade must be strictly perpendicular to the axis of the workpiece being processed.
In the event that you need to cut thin metal with a hacksaw, it is placed between two wooden bars, this “sandwich” is clamped in a vice, and cutting is done together with the bars.
How To Cut Metal. Ace Hardware
Special mention should be made of cutting metal pipes. When cutting them with a hacksaw, there are always fears (especially if the locksmith is not experienced enough) that the hacksaw blade will “go away” and the cut will turn out not in the form of a circle, but in the form of an oval. To avoid this, it is preferable to cut pipes not with a hacksaw, but with a special device. a pipe cutter, in addition to the fact that it gives an even cut, the work with it is also quite productive. The cutting technique is as follows: the pipe is clamped in a vice, fixed disks of the pipe cutter are put on it at a distance of 80-100 mm from the jaws of the vice (at the marking risk), the pipe cutter is installed perpendicular to the pipe axis, by turning the screw handle, the pipe cutter is fixed on the pipe, thereby cutting the movable the cutting roller into the thickness of the metal, with smooth short movements of the pipe cutter handle clockwise-counterclockwise, make a full turn around the pipe, turn the screw V4 turns, again make a full circle with the pipe cutter, and so on until the pipe is completely cut off. To facilitate the work, it is advisable to lubricate stationary discs with soapy emulsion or machine oil.
Sheet metal cutting tools
Initially, when choosing tools, you need to decide on the tasks. It is not only the amount of work that matters, but also the time frame, the accuracy of the cut and the possibility of damage to the protective coating. At a construction site, electric shears are often used. However, you should not expect a very flat edge. The advantage of such a device is the speed of work.
How to cut a sheet of metal straight? At home, the problem is solved quite simply. using scissors for metal. But this method requires a lot of time and physical effort. Scissors will not work if you need to cut long strips. The smoothest cut can be obtained using slotted scissors. Such a tool is quite expensive and is usually used by professionals.
Equipment for cutting profiled and galvanized sheet:
How to cut sheet metal with an angle grinder
One of the fastest ways to cut a galvanized sheet is considered to be cutting with an angle grinder. Among the disadvantages of such processing are torn edges, which will have to be additionally cleaned and leveled. The angle grinder is not suitable for cutting corrugated board, as sparks during cutting can damage the polymer coating. But for simple work that does not require high precision and accuracy, an angle grinder is quite suitable.
Please note that when using such a power tool, purchase a special disc that will not damage the protective coating on the galvanized sheet. After cutting the corrugated board, the edges must be cleaned and covered with a special paint. Such equipment can be used if you are building a shed from a profiled sheet or making a visor. In this case, you do not have to purchase a special and expensive tool.
- choose discs with carbide teeth;
- work at low speeds;
- treat the cut points with a special anti-corrosion coating.
A circular saw
Sometimes a circular saw is used to cut metal. If you work with corrugated board, then the equipment must be turned on at low speeds. Otherwise, the polymer coating may be damaged. To work, you will need a partner who will hold the sheet. Among the advantages of this tool, one can single out the fact that the work is performed without heating, respectively, you will not damage the protective coating on the profiled sheet. It is best to use a circle on aluminum.
To get your circular saw to work quickly, you need to prepare a plywood mold. In this sheet, the groove is not cut out completely. This will be a kind of workpiece that allows you to keep the galvanized or polymer coating on the sheet. An excellent tool for cutting metal is a two-blade saw. It, unlike an angle grinder, does not leave a ragged edge and is much quieter. Unfortunately, not every craftsman has such a tool.
Hacksaw for metal
Many craftsmen have a hacksaw for metal. It is the most versatile and cheapest tool. It should not be used if necessary to cut curly edges, but for making even plates, a hacksaw will do. The biggest drawback of such a tool is the time to carry out the work. You need a lot of it.
Jigsaw
If you need to cut a circle in a sheet of metal, you should use a jigsaw. It works pretty fast, so you can get a neat hole in minutes. Among the disadvantages of the equipment are noise and the possibility of a burnt edge when processing profiled sheets.
- it is necessary to use saws with fine teeth;
- you need to choose a reciprocating mode;
- it is necessary to control the inclination of the cutting part;
- fast failure of consumables.
Wood and metal processing
A hand saw (saw) is a tool designed for cutting thick sheets of strip, round and profile metal, as well as for cutting slots, groins, trimming and cutting out workpieces along the contour and other works. A hand-held locksaw consists of a machine (frame) and a hacksaw blade. At one end of the frame there is a fixed head with a shank and a handle, and at the other end there is a movable head with a tension screw and a nut (wing) for tensioning the blade. The heads have slots into which a hacksaw blade is inserted and fastened with pins.
Frames for hacksaws are made either in one piece (for a hacksaw blade of one specific length) (rarely). or sliding, allowing the fastening of a hacksaw blade of various lengths.
To spread the hacksaw, the knees are bent until the rivet comes out of the cutout and displaced. The rivet is inserted into another cutout and the knees are straightened.
The machine with a movable holder consists of a square with a handle, along which the holder can be moved and fixed in the desired position.
A hacksaw blade is a thin and narrow steel plate with two holes and teeth on one of the ribs. Cloths are made of steel grades: U10A, P9, Kh6VF, their hardness HRC 61. 64. Depending on the purpose, hacksaw blades are divided into manual and machine. The blade is inserted into the frame, teeth first.
The size (length) of a hand-held hacksaw blade is determined by the distance between the centers of the pin holes. The most often used hacksaw blades for hand hacksaws with a length of L. 250. 300 mm, a height of L. 13 and 16 mm, a thickness of h. 0.65 and 0.8 mm.
Each tooth of a hacksaw blade is wedge-shaped. On the tooth, as well as on the incisor, the posterior angle is distinguished, and. taper angle (3, rake angle y and cutting angle 5.a p y = 90 °; a p = 5.
The working conditions of the hacksaw blade differ from the working conditions of the cutter, therefore the values of the angles are different here. When cutting metal of large width, cuts of considerable length are obtained, in which each tooth of the blade removes a chip that looks like a comma. These chips must be positioned in the chip space until the point of the tooth comes out of the cut. The size of the chip space depends on the value of the back angle a, the front angle y and the pitch S of the tooth.
Depending on the hardness of the metal being cut, the rake angle of the teeth of the hacksaw blade can be zero, positive or negative.
The cutting performance of a hacksaw blade with a zero rake angle is lower than blades with a rake angle greater than 0 °.
For cutting harder materials, blades are used, in which the angle of sharpening of the teeth is greater, for cutting soft materials, the angle of sharpening is less. Blades with a large taper angle are more wear-resistant.
For cutting metals, they use mainly hacksaw blades with a pitch of 1.3-1.6 mm, in which there are 17-20 teeth on a length of 25 mm. The thicker the workpiece to be cut, the larger the teeth should be, and vice versa, the thinner the workpiece, the finer the teeth of the hacksaw blade should be. For metals of different hardness, blades with the number of teeth are used: soft metals. 16, medium hardness hardened steel. 19, cast iron, tool steel. 22, hard, strip and angle steel. 22.
When cutting with a hand hacksaw, at least two or three teeth must be involved (cut metal at the same time). To avoid jamming (pinching) the hacksaw blade in the metal, the teeth are set apart.
The setting of the teeth of the hacksaw blade is done so that the width of the cut made with the hacksaw is slightly greater than the thickness of the blade. This prevents the blade from jamming in the cut and greatly facilitates the work.
Depending on the size of the step S, the wiring is done along the blade and along the tooth.
Hacksaw blades with a pitch of 0.8 mm (also allowed for a pitch of 1 mm) must have a set of teeth along the blade (wavy), that is, every two adjacent teeth are bent in opposite directions by 0.25. 0.6 mm. The setting is carried out at a height of no more than twice the tooth height. The routing step is assumed to be 8S.
A blade with a tooth pitch of more than 0.8 mm is spread along the tooth (corrugated spread). With this divorce, with a small tooth pitch, two or three teeth are retracted to the right and two or three to the left. With the middle step, one tooth is withdrawn to the left, the second to the right, the third is not withdrawn. With a large step, one tooth is taken to the left, and the second to the right. Tooth setting is used for canvases with a pitch of 1.25 and 1.6 mm.
The setting of the hacksaw blade should end at a distance of no more than 30 mm from the end.
Preparing to work with a hacksaw. Before working with a hacksaw (hacksaw), the material to be cut is firmly fixed in a vice. The level of metal fastening in the vice should correspond to the height of the worker. Then a hacksaw blade is selected, in accordance with the hardness, shape and size of the metal being cut.
For long cuts, take hacksaw blades with a coarse tooth pitch, and for short cuts, with a fine pitch.
The hacksaw blade is positioned in the slot of the head so that the teeth point away from the handle and not toward the handle. In this case, first, the end of the web is inserted into the fixed head and the position is fixed by laying the pin, then the second end of the web is inserted into the slot of the movable pin and fixed with the pin. Stretch the canvas by hand without much effort (the use of pliers, vices, etc. is prohibited) by rotating the wing nut. At the same time, due to the fear of rupture of the blade, the hacksaw is kept away from the face.
A tightly stretched web with a slight skew and a weakly stretched with increased pressure creates a bend in the web and can cause a break. The degree of tension of the web is checked by lightly pressing a finger on the web from the side: if the web does not bend, the tension is sufficient.
The position of the body of the worker. When cutting metal with a hand hacksaw, they stand in front of the vice straight, freely and steadily, half-turn in relation to the jaws of the vice or the axis of the workpiece. The left leg is slightly put forward, approximately along the mowing line of the cut object, and the body is resting on it. The feet are placed so that they form an angle of 60. 70 ° at a certain distance between the heels.
Hand position (grip). The worker’s posture is considered correct if the right hand with a hacksaw installed on the jaws of the vise (in its original position), bent at the elbow, forms a right angle (90 °) between the shoulder and elbow parts of the hand (Fig. 121, a).
The handle (handle) is grasped with the right hand so that the handle rests on the palm (Fig. 5, b). The handle is wrapped with four fingers, the thumb is placed on top along the handle. Fingers of the left hand grasp the nut and the movable head of the hacksaw.
When cutting with a hacksaw, as well as when filing, strict coordination of efforts (balancing) must be observed, which consists in the correct increase in hand pressure. The movement of the hacksaw must be strictly horizontal. Press on the machine with both hands, but the greatest effort is made with the left hand, and with the right hand, mainly the reciprocating movement of the hacksaw is carried out.
The cutting process consists of two steps:. worker, when the hacksaw moves forward from the worker, and idle, when the hacksaw moves back towards the worker. When idling, the hacksaw is not pressed, as a result of which the teeth only slide, and during the working stroke, light pressure is created with both hands so that the hacksaw moves in a straight line. When working with a hacksaw, the following rules must be followed: short workpieces are cut along the widest side. When cutting rolled angular, tee and channel profiles, it is better to change the position of the workpiece than to cut along the narrow side;. the entire hacksaw blade must be involved in the work;. work with a hacksaw slowly, smoothly, without jerking, making no more than 30-60 double strokes per minute (hard steel. 30-40, medium-hard steel. 40-50, mild steel. 50-60).
At a faster pace, fatigue is more likely to occur and, in addition, the blade heats up and dulls faster:. before the end of the cut, weaken the pressure on the hacksaw, since with strong pressure the hacksaw blade suddenly jumps out of the cut, hitting a vice or part, as a result of which it can cause trauma;. do not allow the blade to heat up when cutting. To reduce the friction of the blade against the walls in the cut, the parts are periodically lubricated with mineral oil or graphite grease, especially when cutting viscous metals;. brass and bronze are cut only with new blades, since even slightly worn teeth do not cut, but slide;. in case of breakage or chipping of at least one tooth, work is immediately stopped, the remnants of the broken tooth are removed from the saw cut, the blade is replaced with a new one or two or three adjacent teeth are ground on the machine and then continue to work.
Cutting sheet metal with your own hands. How to evenly cut a sheet of metal with scrap materials. Cut out the circle and other shapes.
Sheet metal is a common building material used to make fences, drains and canopies. You can often find ready-made galvanized steel products on sale, such as ridge skates or pipes for draining rainwater from the roof. But what if the product is of a non-standard size and you need to cut sheet metal with your own hands?
Wood and metal processing
A hand saw (saw) is a tool designed for cutting thick sheets of strip, round and profile metal, as well as for cutting slots, groins, trimming and cutting out workpieces along the contour and other works. A hand-held locksaw consists of a machine (frame) and a hacksaw blade. At one end of the frame there is a fixed head with a shank and a handle, and at the other end there is a movable head with a tension screw and a nut (wing) for tensioning the blade. The heads have slots into which a hacksaw blade is inserted and fastened with pins.
Frames for hacksaws are made either in one piece (for a hacksaw blade of one specific length) (rarely). or sliding, allowing the fastening of a hacksaw blade of various lengths.
To spread the hacksaw, the knees are bent until the rivet comes out of the cutout and displaced. The rivet is inserted into another cutout and the knees are straightened.
The machine with a movable holder consists of a square with a handle, along which the holder can be moved and fixed in the desired position.
A hacksaw blade is a thin and narrow steel plate with two holes and teeth on one of the ribs. Cloths are made of steel grades: U10A, P9, Kh6VF, their hardness HRC 61. 64. Depending on the purpose, hacksaw blades are divided into manual and machine. The blade is inserted into the frame, teeth first.
The size (length) of a hand-held hacksaw blade is determined by the distance between the centers of the pin holes. The most often used hacksaw blades for hand hacksaws with a length of L. 250. 300 mm, a height of L. 13 and 16 mm, a thickness of h. 0.65 and 0.8 mm.
Each tooth of a hacksaw blade is wedge-shaped. On the tooth, as well as on the incisor, the posterior angle is distinguished, and. taper angle (3, rake angle y and cutting angle 5.a p y = 90 °; a p = 5.
The working conditions of the hacksaw blade differ from the working conditions of the cutter, therefore the values of the angles are different here. When cutting metal of large width, cuts of considerable length are obtained, in which each tooth of the blade removes a chip that looks like a comma. These chips must be positioned in the chip space until the point of the tooth comes out of the cut. The size of the chip space depends on the value of the back angle a, the front angle y and the pitch S of the tooth.
Depending on the hardness of the metal being cut, the rake angle of the teeth of the hacksaw blade can be zero, positive or negative.
The cutting performance of a hacksaw blade with a zero rake angle is lower than blades with a rake angle greater than 0 °.
For cutting harder materials, blades are used, in which the angle of sharpening of the teeth is greater, for cutting soft materials, the angle of sharpening is less. Blades with a large taper angle are more wear-resistant.
For cutting metals, they use mainly hacksaw blades with a pitch of 1.3-1.6 mm, in which there are 17-20 teeth on a length of 25 mm. The thicker the workpiece to be cut, the larger the teeth should be, and vice versa, the thinner the workpiece, the finer the teeth of the hacksaw blade should be. For metals of different hardness, blades with the number of teeth are used: soft metals. 16, medium hardness hardened steel. 19, cast iron, tool steel. 22, hard, strip and angle steel. 22.
When cutting with a hand hacksaw, at least two or three teeth must be involved (cut metal at the same time). To avoid jamming (pinching) the hacksaw blade in the metal, the teeth are set apart.
The setting of the teeth of the hacksaw blade is done so that the width of the cut made with the hacksaw is slightly greater than the thickness of the blade. This prevents the blade from jamming in the cut and greatly facilitates the work.
Depending on the size of the step S, the wiring is done along the blade and along the tooth.
Hacksaw blades with a pitch of 0.8 mm (also allowed for a pitch of 1 mm) must have a set of teeth along the blade (wavy), that is, every two adjacent teeth are bent in opposite directions by 0.25. 0.6 mm. The setting is carried out at a height of no more than twice the tooth height. The routing step is assumed to be 8S.
A blade with a tooth pitch of more than 0.8 mm is spread along the tooth (corrugated spread). With this divorce, with a small tooth pitch, two or three teeth are retracted to the right and two or three to the left. With the middle step, one tooth is withdrawn to the left, the second to the right, the third is not withdrawn. With a large step, one tooth is taken to the left, and the second to the right. Tooth setting is used for canvases with a pitch of 1.25 and 1.6 mm.
The setting of the hacksaw blade should end at a distance of no more than 30 mm from the end.
Preparing to work with a hacksaw. Before working with a hacksaw (hacksaw), the material to be cut is firmly fixed in a vice. The level of metal fastening in the vice should correspond to the height of the worker. Then a hacksaw blade is selected, in accordance with the hardness, shape and size of the metal being cut.
For long cuts, take hacksaw blades with a coarse tooth pitch, and for short cuts, with a fine pitch.
The hacksaw blade is positioned in the slot of the head so that the teeth point away from the handle and not toward the handle. In this case, first, the end of the web is inserted into the fixed head and the position is fixed by laying the pin, then the second end of the web is inserted into the slot of the movable pin and fixed with the pin. Stretch the canvas by hand without much effort (the use of pliers, vices, etc. is prohibited) by rotating the wing nut. At the same time, due to the fear of rupture of the blade, the hacksaw is kept away from the face.
A tightly stretched web with a slight skew and a weakly stretched with increased pressure creates a bend in the web and can cause a break. The degree of tension of the web is checked by lightly pressing a finger on the web from the side: if the web does not bend, the tension is sufficient.
The position of the body of the worker. When cutting metal with a hand hacksaw, they stand in front of the vice straight, freely and steadily, half-turn in relation to the jaws of the vice or the axis of the workpiece. The left leg is slightly put forward, approximately along the mowing line of the cut object, and the body is resting on it. The feet are placed so that they form an angle of 60. 70 ° at a certain distance between the heels.
Hand position (grip). The worker’s posture is considered correct if the right hand with a hacksaw installed on the jaws of the vise (in its original position), bent at the elbow, forms a right angle (90 °) between the shoulder and elbow parts of the hand (Fig. 121, a).
The handle (handle) is grasped with the right hand so that the handle rests on the palm (Fig. 5, b). The handle is wrapped with four fingers, the thumb is placed on top along the handle. Fingers of the left hand grasp the nut and the movable head of the hacksaw.
When cutting with a hacksaw, as well as when filing, strict coordination of efforts (balancing) must be observed, which consists in the correct increase in hand pressure. The movement of the hacksaw must be strictly horizontal. Press on the machine with both hands, but the greatest effort is made with the left hand, and with the right hand, mainly the reciprocating movement of the hacksaw is carried out.
The cutting process consists of two steps:. worker, when the hacksaw moves forward from the worker, and idle, when the hacksaw moves back towards the worker. When idling, the hacksaw is not pressed, as a result of which the teeth only slide, and during the working stroke, light pressure is created with both hands so that the hacksaw moves in a straight line. When working with a hacksaw, the following rules must be followed: short workpieces are cut along the widest side. When cutting rolled angular, tee and channel profiles, it is better to change the position of the workpiece than to cut along the narrow side;. the entire hacksaw blade must be involved in the work;. work with a hacksaw slowly, smoothly, without jerking, making no more than 30-60 double strokes per minute (hard steel. 30-40, medium-hard steel. 40-50, mild steel. 50-60).
At a faster pace, fatigue is more likely to occur and, in addition, the blade heats up and dulls faster:. before the end of the cut, weaken the pressure on the hacksaw, since with strong pressure the hacksaw blade suddenly jumps out of the cut, hitting a vice or part, as a result of which it can cause trauma;. do not allow the blade to heat up when cutting. To reduce the friction of the blade against the walls in the cut, the parts are periodically lubricated with mineral oil or graphite grease, especially when cutting viscous metals;. brass and bronze are cut only with new blades, since even slightly worn teeth do not cut, but slide;. in case of breakage or chipping of at least one tooth, work is immediately stopped, the remnants of the broken tooth are removed from the saw cut, the blade is replaced with a new one or two or three adjacent teeth are ground on the machine and then continue to work.
Cutting round, square and sheet metal with a hacksaw
A hand hacksaw is usually used for cutting thick sheets, strip, round and profile metal, as well as for cutting grooves, slots in screw heads, trimming workpieces along a contour, etc. It consists of a hacksaw / (Fig. 59, a), tension screw with wing nut 2, handle 6 and hacksaw blade 4, which is inserted into the slots of the heads 3 and fastened with pins 5.
Hacksaw machines are of two types. solid
(Fig. 59, a) and sliding, allowing the installation of hacksaw blades of various lengths.
The size (length) of a hand-held hacksaw blade is determined by the distance between the centers of the pin holes. The most commonly used hacksaw blades are 250. 300 mm long.,
13 and 16 mm high, 0.65 and 0.8 mm thick.
The tension of the hacksaw blade in the machine must be adjusted. A weakly tensioned blade skews during cutting, which can cause the teeth to crumble, and then the blade can break. A blade that is too tightly stretched during operation can also break from a slight skew when moving a hacksaw.
Hacksaw blades, depending on the purpose, are divided into manual and machine tools. Hand blades are made of steel grades U10, U10A, U12, U12A, and machine blades are made of steels of grades P9 and ShKh15. On the lower edge of the blade, teeth are cut along the entire length. Each tooth of a hacksaw blade is shaped like a cutting wedge. On the tooth of the hacksaw blade, as well as on the tooth of the chisel, the following angles are distinguished (Fig. 59, b): the clearance angle a, the angle of sharpening p, the rake angle y and the cutting angle 5.
The working conditions of the hacksaw differ from the working conditions of the chisel and cutter, so here it is necessary to take different values of the angles.
When cutting materials of large width, slots of considerable length are obtained, in which each individual tooth of the blade removes chips in the form of a comma. These chips must be positioned between two adjacent teeth in the chip space until the point of the tooth comes out of the slot.
The size of the chip space depends on the value of the clearance angle a, the rake angle y and the pitch of the teeth £.
The taper angle P must ensure that the tooth is strong enough to overcome the material’s resistance to cutting without breaking. Usually this angle is taken equal to 60 °; with harder materials, the angle is slightly larger. The rake angle y has a decisive influence on the chip formation process. For knife teeth-
It is usually taken from 0 (for hard metals) to 12 ° (for viscous metals) for a wok cloth. Tooth pitch for soft and ductile metals (copper, brass) 1 mm, for materials (steel, cast iron) 1.3 mm; for mild steel 1.6 mm. In the practice of manual cutting of metals, they use mainly a hacksaw blade with a pitch of 1.3-1.6 mm, in which there are 17-20 teeth on a length of 25 mm. The thicker the workpiece to be cut, the larger the teeth should be, and, conversely, the thinner the workpiece, the smaller the teeth of the hacksaw blade should be.
When cutting with a hand hacksaw, at least 2-3 teeth should be involved (cut metal at the same time).
To reduce the friction of the hacksaw blade against the walls of the metal being cut, the teeth are set apart in different directions. Depending on the size of the step £ (Fig. 59, a), the setting of the teeth is done in different ways. The teeth with a large step are bent one by one to the right and to the left (Fig. 59, c); teeth with an average pitch are bent one at a time to the right and left, and the third is not bent. The teeth with a small pitch are bent two at a time. three to the left and two or three to the right, while a wavy line is formed, or the so-called corrugated wiring (Fig. 59, d).
The setting of the hacksaw blade should end at a distance of no more than 30 mm from the end.
Corrugated saw blades are less productive and wear out faster. The amount of divorce on the side should exceed the thickness of the web by 0.2-0.5 mm.
Blades for hand hacksaws are made in various lengths 1, 12-15 mm wide and 0.6 to 0.8 mm thick. The most popular canvases should be considered with a length of 250-300 mm.
Methods for cutting metal with a hand hacksaw
Before proceeding with cutting metal, it is necessary to choose a hacksaw blade, in accordance with the hardness, shape and size of the material to be cut.
It is necessary to fasten the blade in a hacksaw so that the tip of the teeth is directed forward along the hacksaw; the blade tension in the hacksaw should be adjusted. When starting to work with a hacksaw, you should firmly fix the material to be cut in a vice. The level of metal fastening in the vice should correspond to the height of the worker. Then stand in front of the vice in half turn, that is, at an angle of 45 ° to the center line of the vice (the distance between the vice and the body of the worker should be 150-200 mm). Leaning on the left leg, set slightly forward, the right should be placed in relation to the left at an angle of 60-70 °. When working, the body should be straight. The hacksaw must be taken with the right hand as shown in fig. 60, a, and with the left hand. by the front end of the hacksaw in order to balance it and get a steady movement during cutting (Fig. 60, b). Keep the hacksaw in a horizontal position while cutting. You need to move the hacksaw smoothly, without jerking, lightly pressing it down with both hands when moving forward. It is generally accepted that the pressure force should correspond to approximately 1 kg per 0.1 mm of blade thickness. At the end of the cut, the pressure should be released.
The normal stroke length of a hacksaw should be such that about 2/3 of its length works, and not just the middle part of the blade.
The speed of the hacksaw depends on the hardness of the material being cut and averages from 30 to 60 double strokes per minute. To reduce friction against the walls of the workpiece being cut, periodically lubricate the blade with thick lard or mineral oil.
In the process of work, the hacksaw blade sometimes “leads” away from the marking; it should not be straightened, as breakage or chipping of the blade teeth is possible. In this case, it is better to start cutting the workpiece from the opposite side.
Chipping of the teeth of a hacksaw blade also occurs from the excessive hardness of the metal being cut, from strong pressure on the blade during cutting of narrow workpieces, the presence of gas bubbles (voids), non-metallic inclusions in the metal, etc. to ensure a smooth transition from broken to intact teeth. It is possible to continue working with a hacksaw with a restored blade only after removing the remnants of broken teeth from the slot.
For a more economical use of hacksaw blades, you should first cut soft metals. copper, aluminum alloys with new blades, and then use them to cut steel or cast iron. Brass and bronze should only be cut with new blades, since even slightly worn blades slide more than they cut.
It is easier to cut flat metal on the narrow side (thickness). In this case, the cutting force is distributed over a smaller area and the cutting is faster. In this case, in order to avoid breaking of the blade, it is necessary that the strip thickness overlaps with at least three teeth. If this cannot be done, then a thin strip is cut along its wide side. Holding the strip in a vice with the wide side, they make a cut on the edge with a file and only after that they start cutting, slightly tilting the hacksaw away from you. In the process of cutting, the slope of the hacksaw is reduced by cutting the entire width of the strip and holding the hacksaw in a horizontal position.
In some cases, when cutting long (high) workpieces, it is not possible to complete the cut due to the fact that the hacksaw machine rests against their end. To eliminate this obstacle, you can reload the workpiece and, cutting into it with a hacksaw from the other end, finish the job. expedient, however, is another method: cut with a hacksaw with the blade turned 90 ° (Fig. 61, a). This way you can cut strips of any length.
When cutting thin sheets or strips, they are placed between wooden bars, clamped in a vice, and then cut together with the bars (Fig. 61, b).
Cutting curved or angular cuts in thin places is done with special knives-
Kami called jigsaws. in which, instead of a hacksaw blade, a narrow thin saw with fine teeth is fixed. They work with a jigsaw “for themselves”. When cutting curly slots with a jigsaw in places where the direction of the cut contour changes, holes are drilled with a diameter equal to the width of the jigsaw saw. Having passed a saw through such a hole, fix it in a frame and continue cutting in a given direction.
Cutting round metal of small sections is carried out with a hand hacksaw. Workpieces with a diameter of more than 50 mm are cut, as a rule, on powered hacksaws, circular saws, cutting and other machines.
The cutting process is reduced to the fact that a marking risk is preliminarily applied on a piece of steel with a circular cross-section. Then the workpiece is clamped in a vice in a horizontal position and a small cut is made with a triangular file at risk in order to cut the hacksaw blade into the metal at a given length along the length. Sometimes, to guide the hacksaw at the beginning of the cut, proceed as follows: at the risks on the workpiece, put the thumb of the left hand, resting the fingernail at the risk, and the canvas-
metal gasket; 4. gasket
Zhovks are pushed close to the nail. Then a hacksaw, supported by the right hand with an extended index finger, creates a stable direction when cutting it into the metal (Fig. 63, a). And only after making sure that the cutting of the hacksaw blade is correct, they get into a working position and continue cutting to the end, preventing the workpiece from breaking off (Fig. 63, b). Breaking off the workpiece is allowed in the case when its ends must be sawn off. In that
In the case of bars (pieces), cuts are made (Fig. 63, c) from two to four sides, and then in a vice or with a hammer through a metal bar, they break (Fig. 63, d).
Cutting square metal is carried out in the same way as round metal, with the only difference that the hacksaw is slightly tilted away from itself at the beginning of the cutting process. As the cut is made, the slope is gradually reduced until the cut reaches the opposite edge of the workpiece. Then they are already cutting with the horizontal positioning of the hacksaw.
Cutting the metal of the shaped section. Before cutting metal of a complex shape, for example, an angular profile, it is necessary to use a square and a scribe to mark the cutting points on both shelves (when cutting the channel, the risk should also be applied on the wall). After that, clamp the metal to be cut in a vice so that the risks of both shelves are visible, and with a triangular file make a small cut along the risk from the corner of the profile base. With the hacksaw blade in the cut, start cutting the profile, holding the hacksaw in an inclined position, and then align it and pro-
Should cut as in the previous case. When cutting the profiles of structural shapes, it is necessary to keep an eye on the direction of the hacksaw at all times, not allowing it to deviate from the marking risks.
In some cases, it is necessary to make slots (slots) in the heads of locking and other screws. For cutting shallow and narrow slots, it is recommended to use a special hacksaw with a thin blade. Wider slots (slots) in the screw heads can be obtained with an ordinary hacksaw with one or two hacksaw blades inserted together into the hacksaw.
Cutting pipes manually is carried out with a hand hacksaw or pipe cutter, and mechanically. on special pipe cutting machines.
The necessary conditions for the correct execution of work on cutting pipes with a hand hacksaw are: marking the places of the cut, choosing a hacksaw blade and observing the basic rules for working with a hacksaw.
The cutting site is marked using a simplified template and a scribe. The template is cut out of thin sheet metal in the form of a rectangular plate bent along a pipe. Then this template is brought to the place of the cut and along its edge a scribe is applied to the circumference of the pipe with a scribe.
The pitch of the teeth of the hacksaw blade should be chosen the smaller, the harder the pipe material and the thinner its wall.
For cutting, the pipe is clamped in a vice in a horizontal position. Thin-walled pipes with a cleanly finished surface should be clamped in a vice between special wooden mouthpieces (Fig. 65, a). They also use pipe clamps with wooden backings, in which grooves are cut along the pipe diameter. Crepe is comfortable-
Casting pipes in chain (Fig. 65, b), screw (Fig. 65, c), and when cutting thin pipes. in special clamps.
When cutting the pipe, hold the hacksaw horizontally and tilt it slightly towards you as the hacksaw blade deepens into the pipe. If the blade is pinched in the slot, remove the hacksaw, turn the pipe 45-60 ° away from you and continue cutting, slightly pressing on the blade.
If, when cutting, the hacksaw leads away from the marking risks, then the pipe must be turned and cut again.
Cutting pipes with a hand hacksaw is a laborious and difficult operation, especially when cutting pipes of large diameters. Cutting with the help of special pipe cutters, devices, etc. is more productive.
The pipe cutter is a special device in which steel disc cutters (rollers) serve as the cutting tool. The most common roller, clamp and chain structures of pipe cutters
The roller pipe cutter consists of a bracket 2 (Fig. 66, a), a screw lever 7 and three disc rollers 4, two of which are mounted on the axles in the bracket 2, and the third is mounted on an axis fixed in a movable bracket 3. The cut pipe is fixed in the clamp 6 with screw 7, after which the pipe cutter is installed on the pipe 5. When the screw lever 1 is rotated to the right, the bracket 3 will move the cutting roller 4 until it touches the pipe wall under some pressure. A pipe cutter with three rollers cuts at the same time in three places, therefore, when working, it is shaken by the lever (about an Uz turn in both directions). To prevent heating of the cutting rollers during operation, the cutting place is lubricated with machine oil, and the cutting is performed without applying-
Nii great effort. Large-diameter pipes are cut with a clamp or chain pipe cutter (Fig. 66, b, c).
The disadvantage of roller pipe cutters is that, during the cutting process, they press the pipe end into the hole and form external and internal burrs, which require additional work to be removed.