Sab. bottom: cut or leave ? (1 online
You use an outdated browser. This and other sites can be displayed in it incorrectly.You need to update the browser or try to use another.
Well-Known Member
Some sources say that over.low frequencies with their inaudibility also overload the sound tract, and in general only the harm from them. Other sources say that, although they are inaudible, they play the role of such a “substrate”, and without them the music sounds poorer on the bottoms. What to do with them ?
Member
Sergecodeq in electronic manufacturers have already thought for us, unless this is an exotic homemade device. If everyone begins the heads of iron, they will not buy this piece of iron. There were no crime in the synthesizers known to me. Stick and write. The main thing is to sound good
Member
I can be. I won’t argue as I don’t know. Well, why all the same they advise cutting frequencies, say from 40 Hz? (or up to 40, as it will be right there?)
How to choose a subwoofer and connect it correctly
Today, few people need a home theater or audio system without high.quality low frequencies. And the most convenient and compact way to get powerful and high.quality bass is the subwoofer. True, not everyone is studying the nuances of using acoustic systems, and therefore they choose, connect, or use subwoofers incorrectly. And now we will tell you how to.
Many years ago, the most popular acoustic design for the speakers was a regular closed box, in which the speakers were mounted. It was simple and convenient, but the problem has arisen. In this format, the ability of the “tambourine” columns directly depends on the dimensions of the case, the larger the lower. And this is not always convenient.
To abandon huge columns-grabs in favor of more compact analogues, manufacturers began to use phase-inverter design. With it, due to the use of low.frequency resonance, you can strengthen the bass in relatively small buildings.
So about a quarter of a century ago, a classic standard was formed. Stereopor (t.n. 2.0) when the acoustics kit includes two columns with phase.inverters. This standard is still popular, but from the beginning, there are 2 zero ones, others begin to gain popularity 2.1 (stereo subwoofer), 5.1 (quadrcentersabwofer), 7.19.1 and t.P., Where is the first digit. the number of channels, and the second indicates the presence of a subwoofer (or several).
When experts conducted a study on psychoacoustics, it turned out that at frequencies below 150 Hz, the human ear practically does not feel the separation of channels. And this means that they are worth dividing for medium and high frequencies, and for low ones you can use one amplifier and one separate low.frequency column. subwoofer.
This scheme turned out to be cheaper, easier and more convenient, especially in constrained conditions. In the scheme with one subwoofer, it was possible to reduce the dimensions of the columns again, for example, for convenient placement on the table. The overall subwoofer could be placed in any convenient place, because the perception of bass practically does not depend on the place of placement of their source.
What characteristics to look at
In addition to subjective sensations from the sound of the subwoofer, you need to pay attention to some characteristics. The main criteria:
The frequency range of most subwoofers is from 30 Hz to 150 Hz, rare devices are able to play 20 Hz, sounds below are already infrasound, which most people do not perceive by ear. Sometimes three subdiapasions are conditionally distinguished. deep (from 20 to 40 Hz), medium (from 40 to 80) and high (from 80 to 150 Hz). Interestingly, the more expensive models are characterized by a narrower range of up to 80-90 Hz, because higher sounds are already able to play good “cream columns” (satellites). In some budgetary cases, the upper boundary of the frequency range can be 160-180 Hz and higher (there is nothing good in this, because at these frequencies the subwoofer will already be knocked against the background of the sound of the stereo system as a whole).
Digging dynamics
If you turn the speaker upside down, it will add a useful volume. Since now the basket will not displace its part. This usually allows you to bring down 1-1.5 hertz in the average box.
There is also separate material about this effect where all aspects of the installation of the subwoofer is disassembled by the magnet out. installing the subwoofer upward upwards.
Corps filling (synthetic winterizer)
I must say that not only a synthetic winterizer can be used as a filler (just more affordable), wool, cotton wool and similar materials are also used.
The features here are as follows. First of all, with the help of filling, the quality of the dynamics in the body is confused. That is, if the bass seems to you echoing (whether it is in the phase intelligence or in a closed box), then you can make it softer by filling. In the case of FI, this can often be used when saba with high their own quality. And you need to bring it a little when the increase in volume will no longer be appropriate.
Well, a decrease in the settings is a concomitant effect and will depend on the amount of filler.
But you should not abuse a filling. Too many will make the sound of the subwoofer deaf (the so.called pillow effect). Also, in the case of use for the phase intercinator, you should not have a filler in the port, as this will negatively affect the effectiveness.
Subsonic
Subsonic. this is the same high.frequency filter (HPF) on saboic amplifiers (often on monoblocks). cuts off infrasound. Install it by default by about 20-25 hz. With in.depth tuning, Sabsonik is set to prevent excessive diffuser stroke. Sinuses are alternately included below the frequency of setting up the subwoofer case and the desired value is selected by observing the size of the diffuser.
Bassboost-increases the volume at a certain frequency, as a rule it is 40-45 Hz. When using Basbust, the chance to burn the subwoofer rises sharply, since the clippus occurs much earlier. In most cases, Bassboost is not needed and if you are a newcomer, then just accept the rule “Basbust, do not touch!””
Experienced people can be used to increase the frequency response shelf to pull the failures at certain frequencies, but this is already deep settings and the effect will not always justify the risk.
X.over
X.over-filter switch. It is present in the case when the amplifier does not provide an adjustment for each filter separately. HPF. cuts from below, LPF. cuts from above, Full / Flat. filters are disconnected.
Phase regulator. is part of an in.depth setup. changes the dynamics phase. There is a fixed switch 0 /180 ° and a regulator 0 °. 180 °. Read a separate topic: Sabwuofer phase. correct setting.
Andrey_Geraskin
Banned
So there are 2 opinions that you need to put a slice 70. ok // and 100 will be much? The sub is still located 4 meters behind me, does not buzz.
Valera
Active Mamber
For music, this location will not go (for cinema is possible). Sube and Satellites should be located on the same line, otherwise you will not catch the phase for sure. About the frequency. Your satellites are reproduced from 65 Hz (he wrote). If you put the frequency of the cut of the Saba 70 Hz, then the range of 65-70 Hz will be played and the sub. and satellites. In this place of frequency characteristics, you will get a hump. There should be switches on the back of your monitors, which just cut certain frequencies. Try to put the same frequency on the Saba as on Satellite. From this and start. Good luck.
Andrey_Geraskin
Banned
So there are 2 opinions that you need to put a slice 70. ok // and 100 will be much? The sub is still located 4 meters behind me, does not buzz.
Valera
Active Mamber
For music, this location will not go (for cinema is possible). Sube and Satellites should be located on the same line, otherwise you will not catch the phase for sure. About the frequency. Your satellites are reproduced from 65 Hz (he wrote). If you put the frequency of the cut of the Saba 70 Hz, then the range of 65-70 Hz will be played and the sub. and satellites. In this place of frequency characteristics, you will get a hump. There should be switches on the back of your monitors, which just cut certain frequencies. Try to put the same frequency on the Saba as on Satellite. From this and start. Good luck.
Romik
New Mamber
Well, why all the same they advise cutting frequencies, say from 40 Hz? (or up to 40, as it will be right there?)
In my opinion, so that there is no porridge. This does not mean that on the master you need to put HPF on `40-50`Hz. Just with bass, you need carefully so the Juno reactor has a song Ice Cube. here bass so bass. Hertz on `20-30` definitely cuts a boot. It makes sense to cut it more likely to `20-30`Hz exclusively with the purpose of cutting out the DC component (frequency of 0Hz) or cut to remove excessive Rumble. The same porridge I talked about. But this is rather a consequence of incorrect information and it is only necessary if there is only a resulting master.
Lost Frequencies feat. Janieck Devy. Reality (Official Music Video)
Yolkin
Member
Garbage to kill small manufacturers
But seriously, it makes sense to use the range that you can control. Ear or belly. It doesn’t matter, the main thing is that the control acoustics to this economy reproduces. Otherwise, it will easily come out on the big sound. If there are doubts. It is better to put an IMHO to hell with everything that does not give in to control. If you go to the car and part of the view is closed (the glass is stuck for example), Duc does not need to be turned blind. Troubles can be
Elimination of turbidity
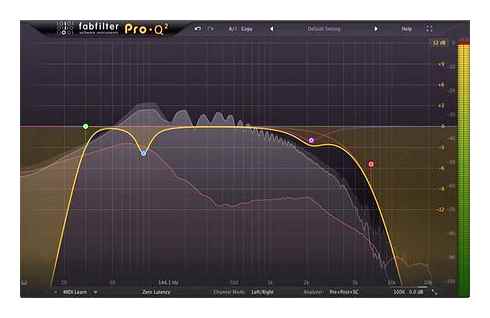
In arrangements with simultaneously playing bass and barrel, it is quite difficult to make friends these tools. Some of them will certainly be lost against the background of a comrade, which is why the dense and strong bottom of the mix will be destroyed. This can be fixed by the Carving Space compensation technique.

The essence of the method is simple: increasing the frequencies of one tool should be compensated by the weakening of the same frequencies of another tool. For example, you strengthened the frequency of 95 Hz at the bass, so the same frequency needs to be mirrored at the barrel. This approach minimizes the collision of the frequencies of these tools. the barrel and the bass will not fight for the same frequency ranges.
You can make such mirror processing by any equalizers installed in your system. If you use the Neutron 2 equalizer, then life becomes even easier: the equalizer provides inversive frequency processing. the plugin will automatically strengthen or loosen the frequency on the neighboring path.
In the image above the barrel, it was chosen as source of disguise (Neutron works on the barrel path). The Feedback button is active. the plugin will automatically loosen or strengthen the bass frequency when processing a kick.
Fast parallel processing
Parallel compression and parallel saturation-popular methods of processing and improvement of bass guitars. To apply these techniques in the DAW, you will need several tires and messages, and the correct routing of the signal. When working with Neutron 2, processing becomes easier: each plugin module is equipped with a MIX master for independent and parallel processing up to 6 effects without any additional settings.
The image shows that each module has its own vertical slider (pay attention to the red place). By the way, the screenshot demonstrates a mixture of aggressive compression and active saturation, whose ratio is tuned to the same mix slider.
What is a cut in auto.sound
The tape recorders from the respected Zanderlex signed that it would be useful and interesting from the.
One of the mandatory stages of sound setting in the car interior is the selection of optimal separation of frequencies between all radiating heads: low.frequency, low.frequency/scores, scores (if there is) and RF. There are two ways to solve this problem.
Firstly, restructuring, and often a complete remake of a full-time passive crossover, secondly, the connection of speakers to an amplifier operating in multi-lane amplification mode, the so-called BI-AMP inclusion options (two-lane amplification) or tri-en (three-lane amplification).
The first method requires serious knowledge of electroacoustics and electrical engineering, therefore, for independent use, it is available only to specialists and experienced radio electrons-amateurs, but the second, although it requires a larger number of amplification channels, is also available to a less prepared car enthusiast.
over, the vast majority of power sold are initially equipped with a built.in active crossover. For many models, it is so developed that with success and quite high quality allows you to realize multi.lane inclusion of AC with a large number of speakers. However, the lack of a developed crossover in an amplifier or a head device does not stop fans of this method of voicing the cabin, since the market presents many external crossovers that can solve these problems.
At first it should be said that we will not give you one hundred percent recommendations, since they do not exist. In general, acoustics are a field of technology where an experiment and creativity is assigned a big role, and in this sense, audio equipment fans were lucky. But to conduct an experiment, so that it does not work out, like that crazy professor. with explosions and smoke. certain rules must be followed. The first rule is not to harm, but about others it will be discussed below.
Most difficulties causes the inclusion of sum and (or) HF components. And the point here is not only that it is these ranges that carry the maximum information load, responsible for the formation of a stereo effect, sound scene, and are also very susceptible to intermodulation and harmonic distortions if the separation frequency is incorrectly set, but also in the fact that this frequency is directly dependent and the reliability of the work of the CTS- and HF Damics.
The selection of the lower boundary frequency of the signal range supplied to the NFA depends on the number of strips of the acoustic system. When a two.lane AC is used, then in the most typical case, t.e. When the low-frequent/contaminet is located in the doorway, to raise the level of the sound scene, it is advisable to choose the boundary frequency as lower as possible. Modern high-quality HF with low resonant frequency FS (800-1500 Hz) can play signals from a frequency of 2000 Hz. However, most of the used heads used have a resonant frequency of 2000-3000 Hz, so it should be remembered that the closer to the resonant frequency we set the separation frequency, the greater the load falls on the HF Damage.
Ideally, with the steepness of the characteristics of the fading of the filter 12 dB/Oct, the variety between the frequency of separation and the resonant frequency should be larger than the octave. For example, if the resonant frequency of the head of 2000 Hz, then with a filter of this order, the separation frequency should be set to 4000 Hz. If you really want to choose the frequency of separation of 3000 Hz, then the steepness of the characteristics of the filter attenuation should be higher. 18 dB/Oct, or better. 24 dB/Oct.
There is another problem that must be taken into account when setting the separation frequency for high-and-dynamics. The fact is that after the coordination of the components according to the reproduced frequency range, you still need to coordinate them in terms of level and phase. The latter, as always, is a stumbling block. it seems to have done everything right, and the sound is “not the same”. It is known that the first.order filter will shift the phase by 90 °, the second. 180 ° (antiphase) and t.D., Therefore, during the setting, do not be too lazy to listen to speakers with different polarity of inclusion.
To the frequency range of 1500-3000 Hz, the human ear is very sensitive, and in order to convey it as well and cleanly as possible, you should be extremely careful. You can break (divide) the sound range in this area, but you should think about how to then correctly eliminate the consequences of an unpleasant sound. From this point of view, a more convenient and safe for configuration is a three-lane acoustic system, and the sum-dynamics used in it allows not only to effectively reproduce the range from 200 to 7000 Hz, but also simply solve the problem of building a sound scene. In the three-lane AS of the NF-Dynamics, they include at higher frequencies-3500-6000 Hz, that is, obviously higher than the critical frequency band, and this allows you to reduce (but not exclude) the requirements for phase agreement.
Before discussing the choice of the frequency of separation of the inter- and low-frequency disabilities, we turn to the design features. Recently, installers have very popular for dome diaphragm. Compared to conical contaminants, they provide a wider orientation diagram and easier in the installation, since they do not require additional acoustic design. Their main disadvantage is a high resonant frequency lying within 450-800 Hz.
The problem is that the higher the lower boundary frequency of a strip of signals supplied to the internamed, the less the distance between the inter- and the low-frequency heads should be, and the more critical where exactly is the non-freestyled residence. Practice shows that dome met-dynamics without any problems with coordination can be included with the separation frequency of 500-600 Hz. As you can see, for most copies sold, this is a rather critical range, therefore, if you decide on such a separation, the order of the dividing filter should be quite high-for example, the 4th.
It should be added that recently domed speakers with a resonant frequency of 300-350 Hz began to appear recently. They can be used, starting with a frequency of 400 Hz, but so far the cost of such copies is quite high.
The resonant frequency of inter-dynamics with a conical diffuser lies in the range of 100-300 Hz, which allows you to use them, starting with a frequency of 200 Hz (in practice 300-400 Hz is more often used) and with a low-order filter, while the low-frequency/CT-Dynamics is completely is exempted from the need to work in the CD. Reproduction without separation between the speakers of signals with frequencies from 300-400 Hz to 5000-6000 Hz makes it possible to achieve a pleasant, high-quality sound.
I welcome everyone who came across Gu Kenwood 304th tell me how to properly set the cuts for this all this
A slice is a smooth attenuation of the signal, higher or lower than a given frequency, and therefore speak from above or below.Order is the smoothness of this attenuation.
The most optimal for the section of the whistle with the Foreign Ministry is the second order. (the higher the order, the cleaner and dead the sound will be :)) for sabs, as a rule, they take as steeply as possible, on average. the fourth.
By the way, I had a Sabor in this regard Zamorok. I share the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Sub at the salon resonance frequency. so to crush the resonance, I had to cut lower and dissolve the order. I cut a 40Hz submarine first order. the current in this situation is not heard. But I think this is a special case and in general terms you are right.
Originally, really front bass workers are able to support so low?
Mids cut from 63 thirds of the order. Intelligent selection of worlds and thorough installation solve
Ummm. How to explain in a nutshell 🙂 🙂 :).For example, if your submarine is cut into 60Hz, let’s say this does not mean that it will not sing above. to sing it will be just quieter. and the higher the frequency of the configuration, the quieter. So this is how quickly it will reduce the volume and determines the filter order.For example, if you cut the subwoofs from 60Hz first order, it means at 120Hz it will sing 6db quieter and 240Hz is already quieter at 12db.If you cut from 60 2m order, then there will already be 120.12db and at 240Hz.24db. and so on. the higher the order, the faster the submarine shuts above the settings. The second order is usually used on amplifiers and gu. On simple amplifiers and radio tape records, you cannot change order. On advanced ones, you can
MIXING: Lower Sub Frequencies EQ. PT 1
Epipen like an Andron Kolader seems to be needed, but no one does not understand fucking))))))
Yes, here you can not steam. If anyone does not understand in the order of slices, then it does not need it and does not need. and who needs it, then they first understand the order and then the current is then set up the system. But this is already on complex installes
Ummm. How to explain in a nutshell 🙂 🙂 :).For example, if your submarine is cut into 60Hz, let’s say this does not mean that it will not sing above. to sing it will be just quieter. and the higher the frequency of the configuration, the quieter. So this is how quickly it will reduce the volume and determines the filter order.For example, if you cut the subwoofs from 60Hz first order, it means at 120Hz it will sing 6db quieter and 240Hz is already quieter at 12db.If you cut from 60 2m order, then there will already be 120.12db and at 240Hz.24db. and so on. the higher the order, the faster the submarine shuts above the settings. The second order is usually used on amplifiers and gu. On simple amplifiers and radio tape records, you cannot change order. On advanced ones, you can
and which one (filter order) is considered better?
There are no better and worst. It all depends on the nuances of your system and the necessary settings. I use the 1st order and the third and third in my drill. The 4th has not yet come in handy
I read the current on the Bassklab today, there you’ll look for everything with thresholds, above 80 Hz or some other figure)