Dimensions and weight
For ease of use, manufacturers produce dowel fasteners in various sizes. The parameters of this product are marked with two numbers. For example, 10 by 80, as well as 30 by 6 or 8 by 160 – the first number in this case shows the size of the diameter in millimeters, and the second number will indicate the length of the dowel. The parameters of the dowel in diameter are in the range from 5 to 23 mm, as for the length, it is in the range from 10 to 160 mm, although there are products with a length of 200 mm, for example, a dowel-nail 10×200 mm.
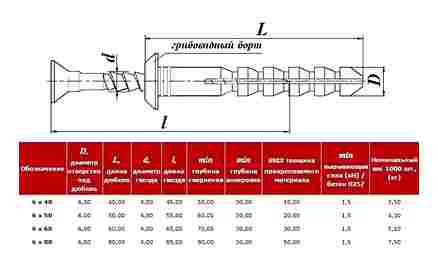
The most common sizes for household use are fasteners 6×40, 5×50 or 5×60 mm, as well as 6×60 mm. For industrial use, dowels of 8×160 mm are often used. When purchasing a dowel-nail, the consumer is faced with the fact that they are often sold by weight, and the mass of products for wholesale or small-scale purchase is indicated not for 1 unit of fasteners, but for 1000 dowels.
All about dowels-nails
- What is it and what is it for?
- Specifications
- Species overview
- Dimensions and weight
- Selection Tips
- Mounting features
When choosing a strong and reliable fastening of a structure to a monolithic surface of a wall, ceiling or floor, dowels are most often used. This type of fastener, in terms of its properties to hold large loads of structures, with the right choice, is compared in terms of reliability with anchor bolts. Dowel fasteners are produced today in various modifications and have different parameters in terms of diameter and length. Focusing on the type of dowel-nail, the methods of its installation are also different..
Species overview
The options for the manufacture of a nail dowel can be with or without a threaded thread, its dowel is made in the form of a plastic body with a secret collar or a cylindrical shape. The nail itself is equipped with a cap, which most often has a mushroom-shaped outline. Along the length of the rod, the nail has a spiral thread, and if the nail is driven, then its surface can be smooth, and there is no plastic cylinder in the fastener design. This type is classified as fire resistant, since the metal, in the absence of plastic, does not support combustion. Some models of the dowel are produced with fitted washers. The washer-shaped spacer itself is initially located at the end of the nail body, and during installation it shifts towards the cap – such fasteners are the most durable to the effects of loads.
Dowels-nails are classified according to the method of installation.
- Installation using a conventional hammer – this method is manual. The body of the nail is threaded – then it is screwed in using a screwdriver, or with a smooth working part – then it is hammered in with a hammer. A threaded nail, if necessary, can subsequently be unscrewed and dismantled, and it is very difficult to dismantle a product without a thread, sometimes it is simply impossible.
- Installation using a construction and assembly gun – in this case, the structure of the nail is distinguished by the presence of a special cuff, but it does not have a plastic expansion cylinder. Such a product allows for quick installation and can withstand heavy loads..
There are many types of fasteners according to the material of application.
- For walls made of aerated concrete – the dowel structure is equipped with ribs in the form of spirals, which wedge at the moment the fasteners are driven into the prepared hole.
- For brickwork or concrete monolith – nylon dowels are used for working with concrete or brick, they can withstand up to 450 kg of load. These models can have dowels with or without a thread, the diameter is in the range of 2-16 mm.
- For slotted with voids or solid mass – such fasteners have a large length, which is 60-360 mm. The design of the spacer at the dowel is made so that when it enters the hollow base, the nail dowel can hook several bridges inside the material, thereby providing a strong hitch.
- For the lathing – such dowels are called distance dowels, and they make it possible to fix the structure of the lathing with a small offset from the wall surface. This distance ranges from 1-30 mm. The dowel is divided into 2 parts, one of which is intended for the structure rail, and the other for the wall. Both parts are connected with a screw.
With this method, it is possible to achieve compensation for wall irregularities and obtain uniform fastening of the structure..
- Universal fastener – its device is capable of self-determination inside the surface during installation. If the fixation has occurred in a dense material, then the dowel body expands, and if the installation is carried out in a hollow material, then when it enters the void area, the structure protrudes and adjoins the support.
- For surfaces with a small thickness – for this purpose, dowel structures made of metal are used. When mounting a steel nail, the metal frame swells and adheres firmly to the area of the thin walls of the material.
- For slatted guides, floor plinths, wall lathing – the nail type of dowel is used. It is indispensable in cases where multiple mounting of fasteners is required. The fastening nail of such a device is equipped with a special knurling. During the installation process, the working part of the screw is inserted together with the dowel into the prepared hole through the crate or rail, and then this pair is driven in with a hammer.
After completing the fastener, it will not be possible to dismantle it if necessary..
- For suspended ceiling structures, a special fastener called a “butterfly” is used, which works on a surface that has voids. When mounted, passing the first dense level of material, under the action of a spring mechanism, the dowel opens its system, thereby resting on the sheathing structure from the inside. The butterfly dowel is provided with hook-shaped protrusions and has a thread.
- For heavy suspended products – the dowel structure is used to work with concrete and brick surfaces in situations where heavy gates or other products need to be fixed on the work surface. Such anchor dowel fasteners will be able to withstand a multi-ton load..
- For foam concrete and gypsum cardboard – both nylon and metal types are produced, which have a drill-shaped tip of the working part, and there is also a thread on the rod of their body. These dowel fittings do not require drilling holes. For example, when you need to fix acoustic material, the entire structure is screwed in with a screwdriver or screwdriver.
- For solid concrete or fixing thermal insulation – for using a dowel, holes in the material are not pre-made, and the fasteners themselves are hammered without a nail.
- For bricks with slotted voids, an injection type of dowel fastener is used. It works with a mesh anchor inserted into the prepared hole, into which a dowel is then driven in, after which a hardening compound is introduced to it using a syringe device. Under the influence of the adhesive, the anchor mesh is destroyed, and a round anchor is formed at this point..
According to the shape of the side or head, the dowel-nail is of 3 types:
- cylindrical;
Various materials for working wall or ceiling surfaces require a thorough approach in the selection of the fastening device. In addition, the size of the dowel-nail itself depends on the type of work performed..
On drywall
Great care is required from the installer when working with this fragile material. First, a hole of the required length and diameter is made in the drywall, and then the dowel fasteners are inserted all the way, lightly tapping on its head with a hammer, after which it is required to screw the screw into the dowel structure with a screwdriver. When working with plasterboard surfaces, you need to measure the mass of the structure attached to them.
If it is quite large and heavy, then it is not recommended to use a dowel-nail, since this type of fastening will destroy the material under the influence of the weight of the structure attached to them.
How to Use a Drill | Using Tools 101 for Beginners | Cordless Power Drill
On a brick
A hole is made in the intended section of the wall surface, and, in order to avoid the formation of cracks in the body of the brick, they begin to drill at low speeds of the drill, gradually increasing them, but only when the depth of the hole reaches 8-10 mm. Before installing the dowel attachment, dust and small brick chips are removed from the hole, and then the dowel is driven in with a hammer.
On concrete
The area for the hole is marked with a center punch, after which they take a perforator and drill the hole to the required depth. The diameter of the drill or drill bit for drilling is required to be taken equal to the diameter of the dowel fastener. As for the length of the hole, it is made 5-6 mm longer than the dowel you have chosen. Further, dust and fragments of material are removed from the hole using a household vacuum cleaner. Then the dowel is hammered into the hole with a hammer, and the screw itself is screwed in or hammered into the dowel structure. When hammering in a screw, you need to leave 3-5 mm of its free edge of the head in order to suspend the mounted structure.
How to Use a Drill
What is it and what is it for?
Dowel fastening is a way of mounting various objects or structures to solid solid surfaces – this is its purpose. It works great on concrete, brick or stone surfaces, and can also be applied to drywall and ceramics. Externally, the dowel-nail looks like a device that combines 2 components: a dowel structure made of plastic and a screw. The construct of certain varieties of the dowel frame has a limiter made in the form of a cuff, which is necessary so that when the dowel is driven into the wall, the device does not sink into the prepared hole. The limiter can be of various modifications – round, in the form of a cylinder or a countersunk type.
It is possible to install dowel fasteners inside the wall using a hammer, while the installation process is simple and does not take much time. This mounting option is used for mounting drywall systems, for installing a plinth or cable channel, hanging shelves, cabinets and much more. The dowel-nail performs reliable fastening only in solid monolithic structures; it is impractical to use it for aerated concrete or hollow bricks.
This is explained by the fact that the dowel-nail does not have such a spacer component that would help it to gain a foothold in the loose material.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR OPERATING THE POWER DRILL
GENERAL PROVISIONS.
- Persons at least 18 years of age who have completed industrial training are allowed to work with the electric drill..
- An electric drill should be issued for work only in good condition, to persons who have an appropriate certificate for the right to use it and who have undergone introductory briefing and instruction at the workplace.
- There should be a first aid kit in the immediate vicinity of the workplace..
BEFORE STARTING WORK.
2.1 Put on overalls and put them in order, fastening or wrapping a wide elastic band around the cuffs of the sleeves, fasten all buttons, personal protective equipment (goggles).
2.2 Inspect the workplace, remove everything from under your feet and from the aisles. If the platform is slippery (icy or oiled), sand should be sprinkled on the platform. The work area must be clean and well lit. Prepare the necessary tools and fixtures.
2.3 Check the sharpness of the drill and the reliability of its fixation in the chuck. The spindle should not vibrate, “beat”.
2.4 Make sure that the drill chuck has a round smooth shape without protruding ends, bolts and nuts..
2.5 Installation of the working tool, adjustment, as well as repairs can be carried out only when it is completely stopped and turned off..
2.6 Check if the workplace is sufficiently lit.
2.7 Check the electrical cable for external inspection.
3. DURING OPERATION.
3.1. It is forbidden to work with an electric drill from ladders, work from a ladder is allowed if there is only a fence and appropriate stops on the legs of the ladder on the entire working platform.
3.2. Do not work in a room containing flammable liquids, gases or dust.
3.3. The device plug must match the socket outlet. Do not make any changes to the plug..
3.4. Avoid contact with grounded surfaces, pipes, heating systems, electric stoves and refrigerators.
3.5. Protect the drill from rain and moisture.
3.6. Clamp the work piece securely.
3.7. Use special drills when drilling grooves or cavities.
3.8. Do not feed the drill with jerks, but smoothly and evenly.
3.9. Do not use your fingers to clean the shavings from the drilled socket. Remove shavings and dust with a brush and furs.
3.10. Do not handle frozen and icy wood.
3.11. Keep an eye on the serviceability of the drill, turn it off immediately if you notice its malfunction, as well as in the following cases:
3.12. a) when the fastening of the drill or the workpiece is loose;
b) when there is a break in the supply of electric current.
3.10. Do not allow unauthorized persons to work.
3.11. Do not touch the electrical wires.
3.12. During operation, DO NOT pull or bend the tool cable..
3.12. When working with an electric drill, workers should generally wear protective goggles..
3.13. During breaks in work, when carrying the electric drill to another place, the tool must be turned off. It is forbidden to leave the electric drill connected to the mains unattended.
3.13. It is forbidden during operation to pull, bend the supply cables of the electric drill. It is not allowed to cross them with ropes, electric cables, electric welding wires that are energized.
3.14. In case of a break in work, a break in electrical wires and all kinds of malfunctions, you must immediately disconnect the electric drill from the mains.
3.15. During rain and snow, working with an electric drill in open areas is allowed only as an exception if there are awnings at the workplace and with the obligatory use of dielectric gloves.
3.16. In especially dangerous rooms and with increased danger when working with an electric drill, the voltage should not exceed 36V.
3.17. The issuance of an electric drill from the pantry directly for work is made with a mandatory entry in the appropriate journal with the signature of the person who received the tool.
3.18. It is prohibited to transfer the electric drill from hand to hand at the workplace..
Only the one who received it from the tool pantry should work with the electric drill..
3.19. IT IS FORBIDDEN:
- operate an electric drill in an explosive room or with a chemically active environment that destroys metals and insulation;
- operate the electric drill in conditions of exposure to drops and splashes, as well as in open areas during rain or snow;
- leave the electric drill connected to the mains unattended;
- operate the electric drill if at least one of the following malfunctions occurs during operation:
- damage to the plug, wire or its protective sheath;
- fuzzy switch operation;
- the appearance of smoke or smell characteristic of burning insulation;
- the appearance of increased noise, knocking, vibration;
- breakage or cracks in body parts, handle;
- damage to the electric drill.
3.20. When operating an electric drill, it is necessary to handle it with care, do not expose to shocks, overloads, dirt and oil products.
3.21. the electric drill must be turned off by the switch in case of a sudden stop (due to the loss of voltage in the network, jamming of moving parts, etc.).
3.22. It is forbidden to work or walk under a suspended load.
4. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS IN EMERGENCY SITUATIONS.
4.1. When working with an electric drill, the following malfunctions may occur:
§ The rotation speed drops to an abnormal value.
§ During operation, bumps or increased noise are heard.
§ Engine housing overheats.
§ Strong engine arcing.
In all these cases, you should immediately stop working, inform the head of the department. DO NOT use a defective tool!
4.2. When working with an electric drill, the following main emergencies may occur:
§ falling of improperly stored or fixed materials, equipment, inventory or tools;
§ explosion of gas cylinders or gas-air mixture in the boiler room;
§ ignition of fuels and lubricants or flammable materials that could lead to a fire or explosion.
4.3. In the event of an emergency or an accident, employees are obliged to stop work, immediately report the incident to the foreman (foreman) and then follow his instructions to prevent accidents or eliminate an emergency situation..
4.4. Workers who are nearby are obliged to immediately report to the scene of the incident on an alarm signal and take part in providing the victim with first aid or eliminating the emergency situation..
4.5. When eliminating an emergency, it is necessary to act in accordance with the instructions of the master (foreman).
4.6. In the event of a fire, you must immediately stop work and take measures to extinguish it..
4.7. Take measures to remove gas equipment from the place of fire.
4.8. Immediately inform everyone working on the site, the foreman (foreman) and the fire brigade and only after that start extinguishing the fire with primary fire extinguishing means.
4.9. When using foam (carbon dioxide, powder) fire extinguishers, direct the stream of foam (powder, carbon dioxide) away from people. If foam comes into contact with unprotected areas of the body, wipe off with a handkerchief or other material and rinse with a solution of soda.
4.10. When using a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher, do not grasp the bell of the fire extinguisher with your hand..
4.11. Internal fire hydrants must be used by a calculation of two people: one rolls out the sleeve from the crane to the place of the fire, the second, at the command of the rolling sleeve, opens the crane.
4.12. It is prohibited to extinguish ignited fuels and lubricants with water..
4.11. When using a felt blanket for extinguishing (in case of fire), cover the flame with a blanket so that the fire from under it does not fall on the extinguishing person.
4.12. When extinguishing a flame with sand, do not raise the scoop or shovel to eye level to avoid getting sand into them..
4.13. It is allowed to extinguish burning objects located at a distance of less than 2 m from the contact network only with carbon dioxide, aerosol or powder fire extinguishers..
4.14. It is possible to extinguish burning objects with water, chemical, foam and air-foam fire extinguishers only after instructions from the work manager or other responsible person that the voltage from the contact network is removed and it is grounded.
4.15. Extinguishing burning objects located at a distance of more than 7 m from the live contact wire can be allowed without removing the voltage. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the jet of water or foam does not touch the contact network and other parts that are energized..
AT THE END OF WORK.
5.1. Tidy up your workplace. Hand over tools and accessories to the tool store..
5.2. Disconnect the electric drill from the mains, assemble the cable and put it in an appropriate place.
5.3. Clean the electric drill and hand it over to the pantry or toolmaker.
5.4. Report all malfunctions, remarks during work to the foreman or a replacement.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR WORKING ON THE LATHE.
1.GENERAL REQUIREMENTS.
1.1. Persons who are at least 18 years old, trained according to a special program, who have access to these works, who have undergone introductory instruction and instruction at the workplace, may be allowed to work on a lathe..
1.2. Directly at the workplace there must be a list of persons admitted to work on the machine.
BEFORE YOU START.
Correct hand position when working with a lathe.
2.1. Check the serviceability of the machine and mechanical control at idle speed, especially the reliability of the brake system. Check the reliability of the grounding contacts. If you find even a weak electric current when you touch the machine, IMMEDIATELY stop working, turn off the machine and report it to the foreman. Prepare the necessary tools and check their serviceability. DO NOT OPERATE with a defective tool..
DURING WORK.
3.1. When working on lathes, the following safety requirements must be met:
(01) Chucks, faceplates and other rotating devices for fastening workpieces should not have protruding parts, nicks or unsealed depressions on the outer surfaces;
(02) the machining area on universal lathes should be shielded by a protective device (screen), both on the side of the workplace and on the opposite side;
(03) fixtures installed on rotating surfaces must be accurately oriented with respect to the axis of rotation;
(04) faceplates of faceplate lathes should be fenced from the workstation side by serviceable folding devices that ensure safety, and the pits should be covered with strong boards (flooring);
(05) when machining in the centers of parts with a length equal to 10 – 12 diameters or more, as well as for high-speed and power cutting of parts with a length equal to eight diameters or more, additional supports (lunettes) should be used;
(06) Machines designed to handle bar stock should be fitted with tubular barriers with sound-absorbing devices to cover the bar along its entire length. Tubular barriers should also be installed on screw-cutting lathes and other machines that are not intended for processing long bar material. In the absence of such barriers, the rods must be pre-cut into workpieces of such length that they do not protrude beyond the spindle. The bar material supplied for processing on machines should not have curvature;
(07) on machines operating on an automatic cycle, the installation and removal of parts should be carried out only at the loading position.
3.2. Sharpening of short cutters should be done using appropriate mandrels.
3.3. The cutter is clamped with the minimum possible overhang of at least three bolts. The machine operator should have a set of shims of various lengths and thicknesses. Use only shims equal to the area of the cutter, place pieces of metal under the cutter, random shims are not allowed.
3.4. When fixing a part in a chuck or using faceplates, grip the part with the cams as much as possible, place the work surface as close to the support or clamping device as possible. It is not allowed that after fixing the part, the cams protrude from the chuck or faceplate beyond their outer diameter. If the jaws protrude, the chuck must be replaced or a special guard installed.
3.5. In a chuck without backing, only short, balanced parts (no more than two diameters long) can be fixed, in other cases it is necessary to use the center of the tailstock for backing up. After fixing the part in the chuck, remove the socket wrench.
3.6. When fixing a part in the centers, it is necessary:
(01) wipe and lubricate the center holes of the part;
(02) check that the dimensions of the taper of the turning center correspond to the center hole of the workpiece;
(03) secure the tailstock and quill securely;
(04) make sure that the part rests on the center with the entire body part of the center hole, do not allow the center to rest against the bottom of the center hole of the part.
3.7. To process a part, you must first turn on the rotation of the spindle, then feed, while the part should be brought into rotation until it comes into contact with the cutter.
When approaching the cutter to the arbor or faceplate, avoid excessively deep feed of the cutter, plunge in should be done smoothly, without impacts.
Before stopping the machine, you must first turn off the feed, move the cutting tool away from the workpiece, and then turn off the spindle rotation.
3.8. When working at high speeds, a rotating center must be used.
3.9. When centering parts on a machine, cleaning, grinding parts with an emery cloth, filing, scraping, etc., the cutter head must be retracted to a safe distance, and when changing the chuck and part, the rear center (tailstock) is also moved back.
3.10. When installing (screwing) a chuck or faceplate on the spindle, under them on the machine, it is necessary to put wooden gaskets with a recess in the shape of the cartridge (faceplate).
3.11. It is forbidden to screw the chuck (faceplate) by sudden braking of the spindle. Screwing the chuck (faceplate) by striking the cams against the stand is allowed only when the chuck is manually rotated, while stands with long handles should be used (for holding by hand).
3.12. WHEN WORKING ON LATHES IT IS FORBIDDEN.
(01) use chucks with worn jaw flats;
(02) use a non-rotating center for high speed cutting;
(03) use the chuck without securing it with breadcrumbs, which prevent self-loosening during reversals;
(04) use a center with worn or clogged cones;
(05) slow down the rotation of the spindle by pressing the hand on the chuck or part;
(06) place parts, tools and other objects on the machine bed and tailstock cover;
(07) to file, polish and sharpen the processed parts without the use of special devices (tools) and methods to ensure the safety of these operations, as well as perform these operations manually on parts with protruding parts, grooves, grooves, and touching hands or clothes to workpiece.
3.13. It is forbidden to work on machines that do not meet the safety requirements set out in paragraph.
FASTENING THE PART AND THE CUTTER.
Install the device securely with coolant and a shield to protect against chips and emulsion splashes.
DO NOT REMOVE chips with bare hands, use a scoop and crochet hook.
When installing the faceplate or chuck on the spindle, first put a wooden prism-stand, lubricate the spindle thread, make sure that the faceplate or chuck is not oiled and does not slip in your hands.
Wear protective goggles when working on brittle metals and when sharpening tools..
Produce examples of the workpiece only when the machine is at a complete stop.
DO NOT ALLOW the chips to wrap around the cutter and the workpiece; remove them in time with a special hook. Do not pass or receive any items through the machine.
During work, do not be distracted and do not talk to other persons.
DO NOT BRAKE the machine by hand by pressing on the chuck or work piece.
DO NOT LEAVE the key in the chuck after attaching and removing the part from the chuck
When machining long parts, to avoid bending and protruding of the part, use rests.
The workpiece protruding from the back of the spindle must ALWAYS be protected.
When sanding the product, DO NOT use a file without a handle, and also DO NOT sandpaper by hand, use special clips..
For any short breaks and absences, STOP the machine, turn OFF the switch.
Timely and accurately place parts and clean the workplace.
REMEMBER that failure to comply with the Safety Rules entails accidents and is considered a violation of the Internal Regulations.
SAFETY REQUIREMENTS IN EMERGENCY SITUATIONS.
4.1. If flammable materials ignite, use a fire extinguisher, sand, earth, or cover the fire with tarpaulin or felt. It is prohibited to pour water on burning fuel and non-disconnected electrical equipment..
4.2. In all cases of detection of fire or its signs (smoke, burning smell), damage to technical equipment or other danger, the machine operator must immediately report to the foreman and leave the danger zone..
4.3. If the lighting suddenly turns off, you must wait for it to turn on. Moving in unlit rooms is dangerous.
4.4. If you find the slightest signs of poisoning or irritation of the skin, mucous membranes of the eyes, upper respiratory tract, you must immediately stop working, inform the master about this and contact the first-aid post.
AT THE END OF WORK:
Stop the machine and turn off the motor.
Remove shavings from the machine, clean it of dust and dirt, wipe and lubricate the rubbing parts of the machine.
Tidy up the workplace, remove the tool to the place designated for its storage.
Instructions for technical equipment when working on machines and power tools
DRILLING INSTRUCTIONS.
1. GENERAL PROVISIONS.
1.1. Persons who are at least 18 years of age, trained according to a special program, who have access to these works, who have undergone introductory instruction and instruction at the workplace, may be allowed to work on the drilling machine..
1.2. Directly at the workplace there must be a list of persons admitted to work on the machine.
2. BEFORE YOU START.
2.1. Tidy up work clothes: button up or tie up the cuffs of the sleeves, put on a hat.
2.2. Inspect the workplace and make sure:
- in the presence of sufficient lighting of the workplace;
- freely available to starting devices;
- the starting device is in good working order;
- in the grounding of the electric motor.
Safety measures when working on a drilling machine.
DURING WORK.
3.1. Work only on a serviceable machine, in the presence of serviceable fences;
use the machine for its intended purpose.
3.2. Keep away from the spindle and cutting tool during work.
3.3. Install the object to be processed correctly and reliably so that it excludes the possibility of its departure, or other violations of the technological process.
3.4. Do not use when operating cartridges and devices with protruding locking bolts, if any, you must protect them
3.5. The workpieces, vices, fixtures are firmly and securely fixed on the table or foundation plate. Fastening with special bolts and parts..
3.6. The vise MUST BE in good working order, the notch of the jaws is not worked.
3.7. Install parts on the machine and remove them from the machine only when the cutting tool is stopped..
3.8. When installing cutting tools, ensure that they are securely and firmly attached. Install when the machine is at a complete stop..
3.9. Lower the spindle when changing tools.
3.10. Do not use a tool with worn out cones, shanks, beware of cutting your hands on the cutting edge of the tool.
3.11. DO NOT hold the part to be drilled with your hands..
3.12. It is FORBIDDEN to work on drilling machines in gloves. Installation and removal of large-sized parts should be carried out in gloves only after stopping the machine..
3.13. In case of tool delay, shank or other tool breakage – TURN OFF THE MACHINE.
3.14. IT IS FORBIDDEN to drill thin strips, plates or other similar parts without fixing them in special devices..
3.15. If the product turns on the table together with the drill, do not try to hold it with your hand, you should stop the machine, make the right direction or take the appropriate device. Stop the machine IMMEDIATELY if the chuck, drill or part is loose. It is FORBIDDEN to fasten a part, fixture or tool while the machine is running..
3.16. Wear safety goggles when drilling into brittle metals.
3.17. When drilling deep holes, periodically pull the drill out of the hole to remove chips.
3.18. Remove chips on the workpiece and table only when the machine is at a standstill.
3.19. When drilling viscous metals, use special drills with chip-breaking cutting.
3.20. Do not stop the turned off machine by pressing on the spindle or chuck, do not touch the drill until it stops.
3.21. Move the cutting tool to the workpiece gradually, smoothly, without impact.
4 SAFETY REQUIREMENTS IN EMERGENCY SITUATIONS.
4.1. If flammable materials ignite, use a fire extinguisher, sand, earth, or cover the fire with tarpaulin or felt. It is prohibited to pour water on burning fuel and non-disconnected electrical equipment..
4.2. In all cases of detection of fire or its signs (smoke, burning smell), damage to technical equipment or other danger, the machine operator must immediately report to the foreman and leave the danger zone..
4.3. If the lighting suddenly turns off, you must wait for it to turn on. Moving in unlit rooms is dangerous.
4.4. If you find the slightest signs of poisoning or irritation of the skin, mucous membranes of the eyes, upper respiratory tract, you must immediately stop working, inform the master about this and contact the first-aid post.
5. AT THE END OF THE WORK.
5.1. Turn off the machine and wait until it stops completely.
5.2. Put the machine and workplace in order.
5.3. Remove tools and accessories, clean the machine from dirt, shavings and foreign objects.
5.4. Wipe off the machine.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR WORKING ON THE SHARPENING MACHINE.
GENERAL PROVISIONS
1.1. The sharpening of the tool is allowed to be performed by a worker who is at least 18 years old, who does not have medical contraindications, who has been trained and instructed at the workplace, who has received permission to work on the machine.
1.2. When working on a sharpening machine, you must wear special clothing tucked in and buttoned up with all buttons, including sleeves.
1.3. The machine must have a safety guard and a protective screen. In the absence of a screen, the worker must wear protective goggles..
Safety precautions when working on a sharpening and grinding machine.
BEFORE YOU START.
2.1. Check the condition and serviceability of the emery machine, accessories and tools necessary for operation;
2.2. Check and adjust the local lighting so that the work area is sufficiently illuminated and the light does not blind the eyes;
2.3. Check the presence, serviceability and strength of fasteners, fences at hazardous places of the emery machine and make sure that the motor housing, protective covers of starting devices are reliably grounded;
2.4. In the event of a malfunction in the machine, notify the master and do not start work until the malfunctions are eliminated;
2.5. It is FORBIDDEN to work on a malfunctioning machine that does not have the necessary guards;
2.6. Before sharpening products, if there are no special protective screens and devices, it is MANDATORY to wear glasses or a protective shield made of transparent material.
3. DURING OPERATION.
3.1. Feed the workpiece to the circle smoothly, without jerking or sharp pressure;
3.2. Protect the circle from possible shock shocks;
3.3. Before stopping the machine, you MUST move the part away from the circle;
3.4. Remove and put on belts on pulleys only after the machine has come to a complete stop..
It is MANDATORY to stop the machine and turn off the electric motor when:
- leaving the machine for a short time;
- temporary suspension of work;
- power outage;
- cleaning, lubricating and cleaning the machine;
- tightening bolts, nuts, wedges, and other fittings;
- adjustment and rearrangement of the handler;
- adjusting, installing and changing tools;
- detecting any malfunction in the equipment.
3.5. DO NOT put your fingers on the handcuff.
3.6. IT IS FORBIDDEN to stand during work in the plane of rotation of the emery wheel; at this time you should stand to the side of the circle.
SAFETY REQUIREMENTS IN EMERGENCY SITUATIONS.
4.1. If flammable materials ignite, use a fire extinguisher, sand, earth, or cover the fire with tarpaulin or felt. It is prohibited to pour water on burning fuel and non-disconnected electrical equipment..
4.2. In all cases of detection of fire or its signs (smoke, burning smell), damage to technical equipment or other danger, the machine operator must immediately report to the foreman and leave the danger zone..
4.3. If the lighting suddenly turns off, you must wait for it to turn on. Moving in unlit rooms is dangerous.
4.4. If you find the slightest signs of poisoning or irritation of the skin, mucous membranes of the eyes, upper respiratory tract, you must immediately stop working, inform the master about this and contact the first-aid post.
AT THE END OF WORK.
5.1. Stop the machine and turn off the motor;
5.2. Remove shavings from the machine, clean it of dust and dirt, wipe and lubricate the rubbing parts of the machine;
5.3. Tidy up the workplace, put the tool in the space provided for
its storage place.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR WORKING WITH THE SANDING MACHINE.
GENERAL PROVISIONS.
To work with a grinder (angle grinder), persons must be at least 18 years old, trained, having studied the operating manual and this manual..
Safety glasses must be worn when working with the sander..
There should be a first aid kit in the immediate vicinity of the workplace..
The tool must be issued only to serviceable persons and only to persons authorized to work with the grinder..
BEFORE STARTING WORK.
2.1 Put on overalls and put them in order, fastening or wrapping a wide elastic band around the cuffs of the sleeves, fasten all the buttons, prepare protective and goggles.
2.2 Inspect the workplace, remove everything from under your feet and from the aisles. If the platform is slippery (icy or oiled), sand should be sprinkled on the platform. Prepare the necessary tools and fixtures.
2.3 Check and make sure the grinder is working properly.
2.4 Check the correct fit of the grinding wheel on the spindle. The sides of the circle must be perpendicular to the spindle axis. The circle must be securely fastened.
2.5 Check if the workplace is sufficiently lit.
2.6 Check the integrity of dielectric gloves and safety goggles.
2.7 Make sure the grounding is connected.
2.8 Check the electrical cable for external inspection.
DURING WORK.
2. Ensure that the grinder is in good condition. Do not allow persons not related to the work performed to the workplace. Wear goggles to protect your eyes from abrasive and metal dust.
3.2. Hold the sander securely and firmly.
3.3. Observe the temperature of the gearbox housing and the electric motor, which should not exceed 600 C above the ambient temperature.
3.4. Do not clean the surface to be treated with your hands; in this case, use a broom or a brush when the machine is turned off..
3.5. In the event of a malfunction in the operation of the machine (break or crack in the abrasive wheel), immediately stop work and inform the master about it.
3.6. When leaving the workplace, even for a short time, disconnect the sander from the power supply..
3.7. AT THE END OF WORK.
- Operate the machine in an explosive room or with a chemically active environment that destroys metals and insulation.
- Operate the machine in dripping and splashing conditions, as well as in open areas during rain or snowfall.
- Operate the machine without a protective cover, which must be installed in such a way as to protect the worker from injury, and the machine from the ingress of processing products into the ventilation openings.
- use cutting or grinding wheels with an expired warranty without testing them for mechanical strength;
- ground the machine;
- bring inside boilers, tanks, power supplies;
- leave the machine connected to the mains unattended;
- transfer the car to persons who do not have the right to use it;
- operate the machine from ladders;
- pull and twist the cord, subject it to stress (for example, put a load on it);
- handle materials containing asbestos, cement, chalk and abrasives;
- operate the machine if at least one of the following malfunctions occurs during operation:
- Damage to the plug, wire or its protective sheath.
- Fuzzy switch.
- Sparking under the brushes, accompanied by the appearance of a circular fire on the surface of the collector.
- The appearance of smoke or an odor characteristic of burning insulation.
- The appearance of increased noise, knocking, vibration.
- Breakage or cracks in body parts, handle.
- Damage to the working tool.
3.8. When using the machine, it is necessary to handle it with care, do not expose to shocks, overloads, dirt and oil products.
3.9. The cord of the machine must be protected against accidental damage (for example, by hanging the cord). Direct contact of the cord with hot and oily surfaces is not allowed.
3.10. When changing a circle, remember:
before installing the circle, the spindle of the machine and the fastening parts must be cleaned of dust and dirt;
after fastening, the grinding wheel should rotate freely (check rotation by hand);
do a test run for about 1 minute without load;
replace the vibrating wheels immediately.
3.11. When cutting, do not skew the wheel in the cutting plane..
3.12. Keep the cooling holes in the gearbox and handle clean and open at all times.
3.13. Connection of auxiliary equipment (transformers, engine-generator set) to the mains and its disconnection must be carried out by persons of the electrical personnel..
3.14. The machine must be turned off by the switch in case of a sudden stop (due to a power failure, jamming of moving parts, etc.).
3.15. The machine must be disconnected from the mains with a plug:
when changing a circle, disassembling;
when transferring a machine from one workplace to another;
during a break in work;
at the end of work or shift.
3.16. It is forbidden to work or walk under a suspended load.
AT THE END OF WORK.
4.1. Tidy up your workplace. Hand over tools and accessories to the tool store..
4.2. Disconnect the sander from the power supply, assemble the cable and put it in an appropriate place..
4.3. Clean the sander and take it to the pantry or toolmaker.
4.4. Report all malfunctions, remarks during work to the foreman or a replacement.
RESPONSIBILITY.
Persons who have violated the requirements of labor protection instructions are brought to administrative responsibility in accordance with the Internal Regulations and current legislation.
Rules for the use of electrical protective equipment when carrying out work in electrical installations
Electrical protective insulating means are designed to ensure the safety of service personnel when performing work in existing electrical installations. Depending on the purpose and type, an electrical protective device can provide both full protection of a person from voltage, and act as an additional protection.
Electrical installations pose a danger in terms of the possibility of electric shock and thermal effects of an electric arc. Every year there are a number of accidents in electrical installations, most of which occur due to non-compliance by workers with labor protection requirements, in particular, improper use of protective equipment when performing work. Therefore, it is very important to know and be able to correctly use electrical protective equipment when performing work on electrical equipment..
Consider the basic rules for the use of various protective equipment that are used in electrical installations.
General recommendations for all electrical protective equipment
Here are the basic rules for the use of electrical protective equipment that apply to all protective equipment.
If it is necessary to work with one or another means of protection, it is necessary, first of all, to check its suitability for use. First, attention is paid to the appearance of the insulating agent. It should be free of dirt, damage to the case, including paintwork.
Each protective insulating device must be periodically tested – a check for suitability for use in electrical installations. Therefore, before applying a protective agent, it is necessary to check its shelf life – the date of the next test on a stamp of the established sample.
If the electrical protective equipment is contaminated, damaged in the case, or it has expired the period of periodic testing, then such protective equipment should not be used, as this could result in electric shock to a person. Such protective equipment must be removed from service for troubleshooting, testing.
The electrical protective equipment that is planned to be used provides its insulating properties only if they are dry. This feature must be taken into account when it is necessary to work in open switchgears, avoiding the use of protective equipment that has gotten wet (drizzle, rain, frost, snow). If it is necessary to perform work in conditions of moisture ingress, electrical protective equipment specially designed for this purpose must be used..
In addition, the protective sealants must be kept clean. This is especially true of dielectric gloves, shoes and other protective equipment, which quickly become unusable if various aggressive liquids, lubricants get on their rubber surface.
Electrical protective equipment above 1000 V with gripping handles are structurally equipped with limit rings. When performing work, it is necessary to take protective equipment by the handles no further than this restricting ring. This is due to the fact that there is a permissible safe distance to live parts and the protective device is designed in such a way that its insulating part (that part that separates the working part from the handle) has a sufficient length, providing protection against electric shock.
It should also be noted that each electrical protective device is designed to operate at a specific voltage. The voltage class is indicated on the body of the protective device, but this value may differ from the voltage value from which the protective device is really capable of protecting a person. Therefore, when testing a protective device, indicate the voltage value up to which this device can be used..
Dielectric gloves serve as the main means of protection against electric shock in electrical installations up to 1000 V and as additional protection in electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V.
Only absolutely dry dielectric gloves are allowed to be used. If the room where they are stored has a high level of humidity, then before working with gloves, they should be dried indoors at room temperature..
Before using gloves, in addition to external examination, checking the date of the next test, it is necessary to check them for punctures. To do this, you need to start twisting them from the edge towards the fingers. In this case, the glove inflates a little and by pressing it is possible to detect possible punctures through which air will escape..
Insulating pliers are used to replace fuses. When replacing fuses with a voltage class higher than 1000 V, in addition to an insulating clamp, dielectric gloves and protective goggles or masks must be used as an additional means of protection. In electrical installations up to 1000 V, you can use only pliers or dielectric gloves together with glasses or masks to replace fuses.
Replacement of fuses should be carried out with preliminary disconnection of the load. The exception is the fuses for those sections of the electrical network in which there are no switching devices, through which the load can be removed..
Voltage indicators are used in electrical installations to check the presence or absence of voltage on live parts.
If the voltage indicator is equipped with a voltage class switch, then before using it, you must make sure that the selected mode is correct..
If it is necessary to check the absence of voltage on live parts, it is necessary to first check the operability of the used voltage indicator. The indicator is tested for operability on those live parts of the switchgear that are under operating voltage. Also, to check the performance of voltage indicators above 1000 V, special devices can be used to test indicators.
Checking the presence of voltage or checking the operation of the indicator must be performed carefully to avoid overlap between phases or one of the phases on the equipment frame or other grounded metal structures of the switchgear.
When checking the absence of voltage, one should take into account the peculiarities of the operation of individual types of voltage indicators. If the voltage indicator is of pulse type, then it works with a certain delay. Before using one or another type of voltage indicator, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the instructions for its operation, which indicate the characteristic features regarding this or that voltage indicator.
When working on electrical installations above 1000 V, voltage alarms can be used as an additional safety measure.
Voltage alarms are mounted on a protective helmet of an employee or on the wrist and are triggered when a person approaches live parts that are energized. Voltage alarms should not be used as a primary means of checking that there is no voltage. For this purpose, only voltage indicators must be used..
If the voltage alarm does not have a built-in health monitoring, then before starting work it must be checked in accordance with the established procedure in compliance with safety measures.
Insulating rods, depending on the design, can be designed for: installing portable protective earthing, performing operations with switching devices, installing insulating pads, replacing fuses, taking measurements.
Before using this or that bar, you need to make sure that it can actually perform this or that operation. It is forbidden to perform the work with the barbell for which it is not provided..
Certain types of insulating rods must be grounded without fail before use. Such rods cannot be used without grounding..
Insulating rods and voltage indicators for voltages above 1000 V can consist of several parts that are connected by a threaded connection. Before using such electrical protective equipment, it is necessary to check the reliability of their threaded connections, in order to avoid incidents when performing work.
Dielectric footwear. boots, galoshes
Dielectric boots and galoshes are designed to protect a person from electric shock to a person in the area of spreading of earth fault currents – from the so-called step voltage. Dielectric footwear also serves as a protective means when it is necessary to ensure the isolation of a person from the ground (floor surface in the room), in this case, the footwear acts as an alternative to a rubber dielectric carpet and an insulating stand.
Dielectric shoes must be carefully inspected for punctures, visible damage before use. When using dielectric shoes, you need to move carefully, avoiding punctures, which is especially important if you need to move in open areas. Damage to the surface of dielectric shoes can lead to electric shock, for example, in the area of step voltage..
Before using a bot or galoshes, it is imperative to check the stamp with the date of the next test, which should also indicate the voltage at which these protective equipment is able to isolate a person from the effects of current.
Insulating tool
Hand tools with insulating handles (screwdrivers, pliers, side cutters, pliers, wrenches, etc.) serve as the main electrical protective equipment when working in electrical installations up to 1000 V without removing the voltage.
In electrical installations above 1000 V, hand tools with insulating handles do not provide safety during work, therefore, if it is necessary to work on high-voltage equipment, it must be disconnected from all sides from which voltage can be applied, ground, install fences and take other measures to avoid the approach of a person to an unacceptable distance to equipment that is energized.
When carrying out work in electrical installations up to 1000 V without removing the voltage, in addition to tools with insulating handles, it is necessary to ensure the isolation of a person from the ground (floor surface), using dielectric carpets, insulating supports or dielectric shoes. Depending on the nature of the work performed, it is necessary to use additional protective maxi or goggles..
Before using a hand tool, it is necessary to inspect it for damage to the insulating part – kinks, cracks, burrs. Hand tools with insulating handles, like other protective equipment, are periodically tested in an electrical laboratory, therefore, before using it, it is also necessary to check the timing of the next test..
Portable protective earthing
To protect a person from accidentally applied voltage, as well as the effect of induced voltage of some power lines, equipment is grounded. electrical connection of live parts with grounded equipment elements, directly with the grounding loop. Grounding is carried out using stationary grounding knives and portable protective grounding.
Stationary earthing knives are a structural element of disconnectors, individual types of cells, chambers with equipment. Portable grounding is a protective device that should be given special attention. This protective device is installed manually or using built-in or removable rods for installing earthing.
Installation of grounding is carried out directly on live parts, which must first be disconnected and make sure that there is no voltage on them.
A lot of accidents happen because before installing grounding, the absence of voltage is not checked on all three phases. The fact is that the switching devices, by means of which the disconnection of a section of the equipment (creating a visible gap) is ensured, can be disconnected incompletely, that is, one of the phases can remain energized, which subsequently, when installing grounding, leads to electric shock.
As mentioned above, before checking the absence of voltage, it is necessary to check the operability of the voltage indicator..
If we are talking about installing portable grounding on equipment above 1000 V, then it is imperative to use special rods, while also using dielectric gloves. To ensure safety, the installation of portable groundings must be carried out by two people, removal is allowed to be done alone.
If this or that section of the power grid is grounded simultaneously by both stationary groundings and portable, then the stationary groundings must be turned on first so that the installation of portable groundings is safe.
Before using portable groundings, it is necessary to inspect them for the integrity of the conductors, clamps, fasteners of the conductors to them. Insignificant, no more than 5%, damage to the cores is allowed.
In order for the portable grounding to fully provide protective functions, it is necessary to correctly select its type, cross-section in accordance with the voltage class and operating currents of the electrical installation section in which the grounding is planned.
In addition to the protective equipment listed above, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment – overalls, shoes, a protective helmet. Depending on local conditions and the nature of the work performed, it is necessary to use protective equipment against the effects of various negative factors.
For example, in an area with a high level of influence of an electromagnetic field, it is necessary to use special protective clothing sets. When carrying out operational switching, use a special protective suit and shield that provides protection against possible effects of an electric arc.
In conclusion, it should be noted that in addition to the knowledge and ability to correctly apply protective equipment when performing work, it is very important to perform the work correctly, deliberately, carefully in order to avoid mistakes and create dangerous situations. Protective equipment cannot provide absolute protection of a person from possible dangerous situations.
An incorrectly selected switching device, incorrect operation and other errors can lead to accidents. Therefore, the issue of safety when carrying out work in electrical installations must be approached comprehensively, taking into account all possible nuances.