Thermal rolling of rental. Classification and field of application
Metal cutting is carried out by cold and heat treatment (cutting) methods. Their choice is determined by the physical and chemical properties of metal and technical and economic indicators.
Thermal cutting is a method of removing the metal from the surface of the body (rental) or separating the metal object into parts by melting it in a given line or volume.
Thermal cutting in the practice of apparatus is used for cutting metal, combined operations of dividing cutting and preparing the edges for welding, for cutting defective sections of the weld, for cutting holes in the body of the apparatus for reinforcement and other operations.
In apparatus for steels of various classes, the following types of thermal cutting are used: oxygen, oxygen-flue and plasma. Thermal cutting is divided into surface string and dividing (volumetric) cutting.
Oxygen cutting is based on the fact that the cut metal heated to high temperature is oxidized in a stream of technically pure oxygen. Acetylene, natural and passing oil production (methane), oil refining (propane, propane-butane mixtures) are used as combustible gases. Oxygen cutting is mainly used for carbon steels.
Oxygen-fluvial cutting includes the process of supplying powder to the zone of the flame nucleus and its combustion. This type of cutting is used for stainless steels and sheets of large thicknesses.
The next type of thermal cutting is plasma. For this process, an electric arc is used and a stream of working gas plasma received in it, the temperature of which is 4-5 thousand degrees. This allows you to process not only structural materials, but also almost any alloys.
Another of the widely used operations is the air-fiber string of metals. This is the most productive way to remove defective places of welded joints, a rustle of the root of the seam, careful removal of entry strips, brackets of tacks. Due to the heat of the electric arc burning between the product and the electrode, the metal is melted and then removed by the air stream, which is supplied from the nozzle holes in the cutter along the forming electrode.
Technology and area of use of oxygen cutting
Among the various methods of thermal cutting, oxygen cutting is quite widespread. The process of oxygen cutting consists in the local heating of the metal to red and subsequent oxidation with a stream of technically pure oxygen. A stream of air emits molten metal. Acetylene is used as combustible gases, less often natural and passing oil production (methane), oil refining (propane, propanobutan mixtures).
The flame consists of two zones: the nucleus (a zone of complete combustion of gas) and a torch (a zone of incomplete combustion). The temperature reaches 3200-3800 0 C.
Когда нагретый участок металла становится красным, открывают струю кислорода. It is very important to control the speed of cutting.
In the process of cutting, there is a diffusion of some elements into the cutting edge (nickel and carbon) and the formation of a zone of thermal influence. Therefore, this layer of material must be removed mechanically.
The scope of oxygen cutting includes mainly carbon steels.
Oxygen-fluvial cutting includes the process of supplying powder to the zone of the flame nucleus and its combustion. Highly alloyed steel, cast iron, copper and aluminum alloys, slagged metal are subjected to such cutting. Powers of a certain composition are used as fluxes. So, for example, for cutting chromium and chromichelic steels, fluxes of the following composition can be used: iron powder, quartz sand, dolomitized limestone, bicarbonate sodium, phosphoric calcium.
Big Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
The process of surface oxygen cutting proceeds only if the direction of movement of the cutter coincides with the direction of the oxygen stream. With uniform movement of the cutter in the direction. a heating flame can be turned off the generated groove. [one]
Surface oxygen cutting process. Like the process of dividing cutting, based on the ability of iron and iron.bearing alloys heated to high temperature (about 1300. 1400), burn in a stream of oxygen. [2]
The processes of surface oxygen cutting depending on the location and movement of the cutter relative to the processed surface can be divided into three main groups: strict, turning and drilling. [3]
The process of surface oxygen cutting is characterized by a large flow rate of cutting oxygen, reaching 80 m3 / hour. In this regard, when the cutting of oxygen from the pipeline, conventional cylinder valves when they use them as cutting on branches of pipelines have an unsatisfactory characteristic. [four]
The process of surface oxygen cutting proceeds only if the direction of movement of the cutter coincides with the direction of the oxygen stream. [5]
The advantage of the process of surface oxygen cutting compared to other methods of removing the surface layers of the metal is high productivity, which allows you to remove a manual cut of up to 5 kg of metal per minute. [6]
The advantage of the process of surface oxygen cutting compared to other methods of removing the surface layers of the metal is high productivity, which allows you to remove a manual cut of up to 5 kg of metal per minute. At the same time, with superficial oxygen cutting, a layer of metal, adjacent to the surface to be treated, quickly heats up and cools, as a result of which in high.carbon and alloy steels can occur on the surface of the crack. [eight]
The essence of the process of surface oxygen cutting is that the cutting stream of oxygen burns the metal on the surface, forming a rounded groove. [9]
The advantage of the process of surface oxygen cutting compared to other methods of removing the surface layers of the metal is high productivity, which allows you to remove with a cerses up to 5 kg of metal per minute. [ten]
In the process of surface oxygen cutting (cleaning), the surface of the processed metal is heated by a stream of slag and a heating flame of the cutter. [eleven]
The general type of surface oxygen cutting process is shown in FIG. Examples. the use of surface oxygen cutting are shown in FIG. [12]
The characteristic positive features of the process of surface oxygen cutting in comparison with other methods of removing surface defects are: high performance that allows you to remove with a manual cut of up to 5 kg of metal per minute; identification of defects that are clearly indicated after the passage of the cutter; Lack of sticking on treated surfaces. [fourteen]
What is the essence of the process of surface oxygen cutting. [fifteen]
Big Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
Surface oxygen cutting process. Like the process of dividing cutting, based on the ability of iron and iron.bearing alloys heated to high temperature (about 1300. 1400), burn in a stream of oxygen. [31]
The processes of surface oxygen cutting depending on the location and movement of the cutter relative to the processed surface can be divided into three main groups: strict, turning and drilling. [32]
The process of surface oxygen cutting is characterized by a large flow rate of cutting oxygen, reaching 80 m3 / hour. In this regard, when the cutting of oxygen from the pipeline, conventional cylinder valves when they use them as cutting on branches of pipelines have an unsatisfactory characteristic. [33]
The process of surface oxygen cutting proceeds only if the direction of movement of the cutter coincides with the direction of the oxygen stream. [34]
The process of surface oxygen cutting proceeds only if the direction of movement of the cutter coincides with the direction of the oxygen stream. With uniform movement of the cutter in the direction. a heating flame can be turned off the generated groove. [35]
For manual surface oxygen cutting in the industry, rezaki, different in design and area of use. [36]
With superficial oxygen cutting, a decrease in oxygen purity leads to a decrease in the size of the resulting groove and a deterioration in its surface. The numerical characteristics of the effect of the purity of oxygen in this case are very close to the above for dividing cutting. [37]
With superficial oxygen cutting, almost all the heat of the metal oxidation reaction is concentrated on the surface to be treated, while with a dividing, a sharply significant part of the heat is immediately removed from the cut with outgoing gases and slag. [38]
With superficial oxygen cutting, a decrease in oxygen purity leads to a decrease in the size of the resulting groove and a deterioration in its surface. The numerical characteristics of the effect of the purity of oxygen in this case are very close to the above for dividing cutting. [39]
With superficial oxygen cutting, almost all the heat of the metal oxidation reaction is concentrated on the surface to be treated, while during dividing cutting a significant part of the heat is immediately removed by the cutting gases and slag. [40]
With superficial oxygen cutting, a decrease in oxygen purity leads to a decrease in the size of the resulting groove and a deterioration in the quality of its surface. The numerical characteristics of the effect of the purity of oxygen in this case are very close to the above for dividing cutting. [41]
VNIIAVTOGEN, surface oxygen cutting. [42]
How the surface oxygen cutting of metals is carried out. [43]
Surzacs for surface oxygen cutting provide the removal of captivity, shells, sunsets, slag inclusions and other local defects on steel ingots, shaped castings, etc. These cutters also allow you to remove defective sections of welds on low-carbon and low alloy steels and perform U-shaped preparation of the edges of sheets for subsequent welding. If necessary, surface cutters can be used for dividing cutting steel up to 500 mm thick. In all cutters, an injector device is used to prepare a combustible mixture. The barrel body containing the mixing device has a handle with nipples for connecting the sleeves of combustible gas and oxygen, adjusting valves of these gases and a launch valve for cutting oxygen. The tip is attached to the barrel. [45]
Big Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
Surface oxygen cutting is used, for example, for rough string and turning. With a strip, the Rezak makes progressive straightforward movements, as a result of which a rounded groove is cut out from the surface. Removing the layer from the surface of the metal can be carried out both in several passages of one cutter, and in one passage of several cutters, strengthened in the caliper of a mechanized device. The depth and width of the grooves can be different, depending on the used cutting mode and tilting the cutter to the metal surface. [one]
Superficial oxygen cutting can give a significant production effect at a number of enterprises with its proper use, in particular, instead of pneumatic cutting. [2]
Surface oxygen cutting can have a significant production effect in case of its proper use, in particular, in return for pneumatic cutting. [3]
Surface oxygen cutting is used to remove the layer of metal from the surface of the processed part by means of the cutting stream of oxygen directed at an angle of 10. 30 to this surface. [four]
Surface oxygen cutting differs from dividing cutting in that instead of a through cut, a groove forms on the surface of the processed metal. Its profile depends on the shape and size of the output channel for cutting oxygen in the mouthpiece, as well as cutting and location (angle of inclination) of the cutter relative to the sheet. The essence of the processes of dividing and surface cutting is the same. The source of metal heating is not only the heating flame of the cutter, but also the molten slag, which, spreading along the surface of the sheet along the cut line, warms up the underlying layers of the metal. Therefore, with surface cutting, the heat released as a result of iron oxidation is better used than during dividing cutting. [5]
Surface oxygen cutting can be used to clean up defects on the surface of highly alloy steels. In this case, oxygen-fluvo cutting should be used in combination with a surface harsh. For these purposes, cutting of the RPA type or others with oxygen-fluid equipment and installation of the type of UGPR are used. [6]
Surface oxygen cutting differs from dividing cutting in that instead of a through cut, a groove forms on the surface of the processed metal. Its profile depends on the shape and size of the output channel for cutting oxygen in the mouthpiece, as well as cutting and location (angle of inclination) of the cutter relative to the sheet. The essence of the processes of dividing and surface cutting is the same. The source of metal heating is not only the heating flame of the cutter, but also the molten slag, which, spreading along the surface of the sheet along the cut line, warms up the underlying layers of the metal. Therefore, with surface cutting, the heat released as a result of iron oxidation is better used than during dividing cutting. [7]
Surface oxygen cutting can be used to clean up defects on the surface of highly alloy steels. In this case, oxygen-fluvo cutting should be used in combination with a surface harsh. For these purposes, cutting of the RPA type or others with oxygen-fluid equipment and installation of the type of UGPR are used. [eight]
Superficial oxygen cutting is an effective method of processing of steel, which is widely used in industry and is increasingly widespread every year, especially at metallurgical plants when cleaning black rolling. [9]
Superficial oxygen cutting of the MCET is used to clean up defects on the surface of highly alloyed stages. In this case, oxygen-fluvo cutting should be used in combination with a surface harsh. [ten]
Superficial oxygen cutting. Leading materials VNIIAVTOGEN. [eleven]
Superficial oxygen cutting is widely used in the metallurgical industry to remove surface casting defects, in welding production for cutting defective sections of the seams and when performing repair work. [12]
Superficial oxygen cutting is widely used in the metallurgical industry to remove surface casting defects, in welding production for cutting defective sections of the seams and when performing repair work. The process of surface oxygen cutting proceeds only if the direction of movement of the cutter coincides with the direction of the oxygen stream. With uniform movement of the cutter in the direction of the generated groove, the heating flame can be turned off. [fourteen]
Superficial oxygen cutting is widely used in metallurgy when removing surface casting defects, in welding production when selecting defective sections of the seams and when performing repair work. [fifteen]
How To Cut With A Torch/Oxy-Acetylene Cutting Torch
Requirements for metal subject to oxygen cutting
From the requirements it becomes clear that not all metal structures amplified by oxygen cutting. So, aluminum, cast iron, copper and their alloys do not satisfy the above requirements. But oxygen cutting low.carbon steels lends itself to oxygen. The medium and high-carbon steels are also cut quite well, in some cases it is enough to ensure their preliminary heating.
It is very important to use oxygen with purity at least 98.5%for cutting, since with its decrease, oxygen consumption increases significantly and cutting performance decreases.
Basic information about the technique of oxygen cutting
When performing dividing oxygen cutting, it is necessary to take into account the requirements for the accuracy of cutting and the quality of the cutting surface. The preparation of metal for cutting has a great impact on the quality of the cutting and the performance of cutting. Before cutting, the sheets are fed to the workplace and laid on the lining so as to ensure unhindered removal of toxins from the cutting zone. The gap between the floor and the lower leaf should be at least 100-150 mm. The surface of the metal before the sharp must be cleaned. In practice, scale, rust, paint and other contaminants are removed from the surface of the metal with a heating zone of cutting with a gas flame, followed by stripping with a steel brush. Cut parts are marked with a metal ruler, damn and chalk. Often a cut sheet is submitted to the workplace of the cutter already marked.
Before the start of oxygen cutting, the gas cutter must establish the necessary gases pressure on acetylene and oxygen reducers, select the necessary numbers of external and internal mouthpieces, depending on the type and thickness of the cut metal cut.
The process of oxygen cutting begins with heating of the metal at the beginning of the cut to the temperature of the metal of the metal in oxygen. Then the cutting oxygen is allowed (there is a continuous oxidation of the metal throughout the thickness) and the cutter is moved along the cutting line.
The main parameters of the oxygen cutting mode are: the power of the heating flame, the pressure of the cutting oxygen and the speed of cutting.
The power of the heating flame is characterized by the consumption of combustible gas per unit time and depends on the thickness of the cut metal. It should ensure rapid heating of the metal at the beginning of cutting to the ignition temperature and the necessary heating in the process of cutting. For cutting metal up to 300 mm thick, normal flame is used. When cutting a metal of large thicknesses, the best results are obtained when using flame with an excess of fuel (scums). At the same time, the length of the visible flame torch (a closed oxygen valve) should be greater than the thickness of the cut metal.
The choice of pressure of cutting oxygen depends on the thickness of the cut metal, the size of the cutting nozzle and. oxygen purity. With an increase in oxygen pressure, its consumption increases.
The cleaner the oxygen, the less its consumption per 1 pog. m cut. The absolute value of oxygen pressure depends on the design of the cutter and mouthpieces, the resistances in oxygen supplying reinforcement and communications.
The speed of moving the cutter must correspond to the combustion rate of the metal. The stability of the process and the quality of the cut parts are dependent on the speed of cutting. Small speed leads to the member of the cut edges, and the large. to the appearance of re.re.re.re.cut. The speed of cutting depends on the thickness and properties of the cutting sections. The speed of cutting depends on the thickness and properties of the cut metal. When cutting steels of small thicknesses (up to 20 mm), the speed of cutting depends on the power of the heating flame. For example, when cutting steel with a thickness of 5 mm, about 35% heat comes from a heating flame.
a. the speed of cutting is small, b is the optimal speed, c. the speed is high
Figure 1. The nature of the ejection of slag
The speed of oxygen cutting is also affected by the cutting method (manual or machine), the shape of the cutting line (rectilinear or curly) and the type of cutting (procurement or finishing). Therefore, the permissible cutting speeds are determined experimentally depending on the thickness of the metal, type and method of cutting. With the correctly selected cutting speed, the cutting line of the cut should not exceed 10-15% of the thickness of the cut metal.
Figure 1 schematically shows the nature of the release of slag from the section. If the velocity of oxygen cutting is small, then there is a deviation of the bundle of sparks in the direction of cutting (rice. 1, a). With an overstated cutting speed, the deviation of the bundle of sparks occurs to the side reverse of the cutting (rice. 1, c). The speed of moving the cutter is considered normal if the bundle of sparks will come out almost parallel to the oxygen stream (rice. 1, b).
The width and purity of the cut depend on the method of cutting. Machine cutting gives a cleaner edge and lower cut width than manual. The larger the thickness of the cut metal, the greater the roughness of the edges and the width of the cut. Depending on the thickness of the metal, the estimated cut width is:
At the beginning of oxygen cutting, the mouthpiece is placed perpendicular to the surface of the metal or with a small inclination (5-10 °) to the side, the reverse direction of cutting. As the metal of the metal is deepened, the effect of the heating flame weakens, the velocity of the oxygen stream decreases, therefore, during cutting, the cutting stream lags, the lag increases with an increase in the speed of cutting, the lag can be compensated by the downhill in the direction of movement.
Oxygen-dug and air-antigod
The essence of the oxygen-dug cutting is that an electric arc is excited between the electrode and the cut work, which carries out the melting of the metal. Metal removal of cutting is carried out by a stream of oxygen or air.
With oxygen-dug cutting, oxygen enters the cut through the inner channel of the metal electrode (rice. four.4), coated with a special composition.
Rice. four.four. Oxygen-duma cutting scheme:
1— источник электропитания; 2 — направляющая; 3 — электропривод; 4 — разрезаемый металл; 5 — электрод
Рукоятка горелки обеспечивает закрепление электрода и подачу кислорода. Резка начинается с возбуждения дуги между электродом и металлом, затем в рез подается кислород, осуществляющий окисление металла в резе и принудительное удаление продуктов реакции из полости реза. Режущая струя кислорода следует за электродом.
Кислородно-дуговой резкой можно резать углеродистые, легированные, коррозионностойкие стали, чугун, цветные металлы. Резку ведут трубчатыми стальными электродами и тугоплавкими неметаллическими (графитовыми, угольными), а также обычными стальными покрытыми электродами на постоянном и переменном токе.
При подводной кислородно-дуговой резке применяют плавящиеся и неплавящиеся электроды. Плавящиеся электроды изготовляются из стальных трубок наружным диаметром 8 мм, с толщиной стенки 2—2,5 мм длиной 400 мм. На поверхность трубки наносят водоупорное покрытие, которое позволяет опирать электрод на поверхность металла, чем обеспечивается постоянство расстояния между электродом и металлом и стабильность горения дуги. Расход электродов при резке высокий (примерно 1 шт. в 1 мин), поэтому при резке металла под водой применяют карборундовое покрытие, увеличивающее время работы одним электродом до 40 мин. При резке на воздухе применяют полые угольные или графитовые электроды, обеспечивающие значительную экономию металла по сравнению с применением металлических электродов.
Воздушно-дуговую резку металлов выполняют сплошным угольным или графитовым электродом, закрепляемым в электрододержате- ле. В неподвижной губке электрододержателя просверлены отверстия для подачи воздуха параллельно оси электрода.
Различают два вида воздушно-дуговой резки — разделительную и поверхностную. При разделительной резке электрод углублен в полость реза (рис. 4.5, а) под углом к поверхности разрезаемого металла 60—90°. При поверхностной воздушно-дуговой резке дуга горит между концом электрода и поверхностью обрабатываемого металла. Электрод наклонен к поверхности под углом 30° в сторону, обратную направлению резки (рис. 4.5, б). Резку выполняют на постоянном токе обратной полярности. При этом напряжение на дуге составляет 45—50 В, сила тока 250—500 А (для отдельных резаков — до 1600 А), диаметр электрода 6—12 мм. Давление воздуха 0,4—0,6 МПа, расход воздуха 20—40 м 3 /ч, масса выплавляемого металла до 20 кг/ч.
Кислородно-дуговые и воздушно-дуговые способы разделительной резки не обеспечивают высокого качества поверхности реза, поэтому их применяют лишь в тех случаях, когда не требуется высокое качество поверхности реза или имеются затруднения с горючим газом.
Наибольшее распространение получила поверхностная воздушнодуговая резка при выборке дефектов сварных швов, удалении дефектов на стальных, чугунных и цветных отливках. Поверхностная воздушнодуговая резка высоколегированной стали и чугуна конкурирует с поверхностной кислородно-флюсовой резкой высоколегированных сталей и чугуна, так как при ее применении не требуется флюс, горючий газ и кислород.
How to Hand-Torch a Circle with Oxy Acetylene into Metal Tube Steel
Кислородная резка оборудование
Резаки
Для кислородной резки с применением ацетилена используют оборудование для ацетиленовой сварки, но вместо сварочной горелки применяют газовый резак, обычно инжекторного типа, рис 6.
Кислород по рукаву, надетому на кислородный ниппель 1, поступает в резак. Часть кислорода, проходя вентиль 2 и инжектор 10, идет в смесительную камеру 9. Остальная часть кислорода (режущий кислород) направляется в головку 5 через вентиль 3 и трубку4. Из головки резака режущий кислород проходит через центральный канал внутреннего мундштука 6 и поступает к месту реза.
Ацетилен подводится в резак по рукаву, надетому на ниппель 12. Затем ацетилен проходит через вентиль 11 и по пазам инжектора, находящимся на его наружной поверхности, поступает в смесительную камеру 9. Ацетилен в смесительную камеру подсасывается кислородом, проходящим через центральное отверстие инжектора. В смесительной камере образуется горючая смесь, которая проходит по трубке 8 в головку резака, откуда через кольцевой зазор между наружным мундштуком 7 и внутренним
мундштуком 6 выходит наружу. На выходе горючую смесь поджигают, и при этом образуется подогревающее пламя.
Для ручной разделительной резки широко применяют резаки типов «Пламя.62» и РГС.60М. Резак РГС-60М вставной, его присоединяют к стволам сварочных горелок «и ГС-3. Техническая характеристика резака «Пламя.62» приведена в таблице 8.
Для резки с применением газов – заменителей ацетилена применяют резак РЗР-62.
Кроме этих резаков применяют также универсальный резак РУ-66. Универсальный резак предназначен для ручной резки с использованием подогревающего пламени, образуемого смесью ацетилена или газов – заменителей ацетилена с кислородом.
Резак РУ-66 выпускается в трех исполнениях : РУ – для резки стали с использованием в качестве горючего ацетилена и газов – заменителей; РУА- для резки стали с использованием в качестве горючего только ацетилен; РУЗ – для резки стали с использованием в качестве горючего газов – заменителей ацетилена.
Помимо резаков, предназначенных для разделительной резки,
существуют резаки специального назначения для поверхностной резки, например резаки типа РАП-62,РПА-62,и РПК-62.
Резак 321(РАП). табл 9. используют для удаления провисания корней сварных швов, а также мелких дефектов на отливках. В качестве горючего газа для этого резака используют ацетилен.
Резаки РПА-62 и РПК-62 используют для удаления дефектов сварных швов, для чашеобразной подготовки кромок листов под сварку и для удаления местных дефектов на отливках и прокате табл 10.
Для срезания головок заклепок применяют вставной резак РАЗ-60, который присоединяют к стволам горелок «и ГС-3.
Для резки стали большой толщины (до 700 мм) применяют специальную установку УРР-700. Эта установка предназначена для кислородной резки отливок, проката, поковок, отрезки прибылей стального литья и разделки крупного стального лома.
В комплект установки входят: резак РР-700 инжекторного типа, кислородная рампа из десяти баллонов, рамповый кислородный редуктор и ацетиленовая трехбалонная рампа с обычным баллонным редуктором. Для подогреваемого пламени в качестве горючего газа используют ацетилен.
Переносные и стационарные машины предназначены для разделительной резки стали, они отличаются высокой производительностью и чистотой получаемого реза.
Переносная машина «Спутник» предназначена для резки стальных труб диаметром до 1100 мм. Машина может резать трубы перпендикулярно к образующей или наклонно со скосом кромок под углом до 35 ᴼ. При установке на машину двух резаков можно вырезать кольца. Машина имеет тележку самоходного типа с электродвигателем и комплектуется выпрямительным блоком с магнитным усилителем.
Управление магнитным усилителем расположено вне машины.
Машина АСШ – стационарная, предназначена для кислородной резки стали толщиной до 100 мм. Машина в основном применяется для вырезки деталей и заготовок различной конфигурации из листовой стали по специальным шаблонам- копирам. По шаблонам можно вырезать заготовки для гаечных ключей, фланцы, грубые плоские зубчатые колеса и другие детали с допуском 0,3-0,5 мм.
Кислородная резка технология
При разделительной резке поверхность разрезаемого металла должна быть очищена от ржавчины, окалины, масла и других загрязнений. Разделительную резку обычно начинают с края листа. Вначале металл разогревают подогревающим пламенем, а затем пускают режущую струю кислорода и равномерно передвигают резак по контуру реза. От поверхности металла резак должен находиться на таком расстоянии, чтобы металл нагревался восстановительной зоной пламени, отстоящей от края ядра на 1,5 – 2 мм. Для резки тонких листов (толщиной не более 8-10 мм)
Применяют пакетную резку. При этом листы плотно укладывают один на другой и сжимают струбцинами. Значительные воздушные зазоры между листами в пакете ухудшают резку.
При поверхностной резке с обрабатываемого изделия срезают (сострагивают) часть металла, поэтому этот процесс резки иногда называют поверхностной газовой строжкой. Для поверхностной резки применяют специальные резаки. Угол наклона резака к плоскости обрабатываемого металла приповерхностной резке зависит от равномерности передвижения резака. Резак передвигают равномерно, сохраняя постоянный угол наклона к плоскости металла.
Поверхностная кислородная резка металла: особенности и применение
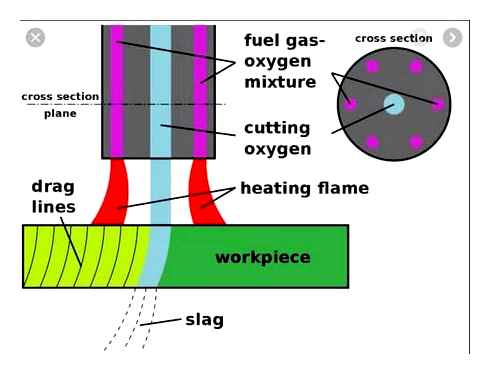
Кислородная резка металлов может быть не только разделительной, но и поверхностной. В первом случае, на металлическом листе или детали появляется сквозной рез. Во втором— результатом обработки является появление на поверхности металла канавок, имеющих в поперечном сечении округлую, квадратную или параболическую форму. В обоих случаях (в отличие от процесса плазменной резки металла ) обработка предварительно разогретой поверхности объекта осуществляется с помощью струи кислорода.
При разделительной резке струя кислорода, выходящая из резака, направляется перпендикулярно обрабатываемой поверхности, либо под углом 45 градусов. При поверхностной резке угол атаки кислородной струи поддерживается равным 10– 30 градусам. Кроме того, при поверхностной резке используется относительно небольшое давление струи кислорода (как правило, не больше 4– 5 килограмм на квадратный сантиметр). Аппарат для поверхностной резки обеспечивает меньшую скорость выхода режущей струи и имеет большую площадь сечения выходного канала. При таких параметрах обработки получается шлак с большим процентным м железа. Это позволяет быстрее разогревать поверхность обрабатываемого металла, что положительно влияет на скорость процесса обработки.
Поверхностная кислородная резка применяется преимущественно в металлургической промышленности. Возможность не только делать канавки в металле, но и снимать весь его внешний слой, делает эту процедуру незаменимой в тех случаях, когда необходимо зачистить холодный или горячий металл перед процессом прокатки. Ручную поверхностную резку используют также для зачистки поверхностных неровностей литья перед заваркой. Кроме того, эта процедура применяется для очистки корня сварного шва и выявления его внутренних пороков до того, как наложены подварочные валики. Как вспомогательный процесс, поверхностная кислородная резка используется при изготовлении сварных конструкций и ремонте литья.
Все права защищены © AJAN (Ажан) 2011. 2022 Тел: 7 (495) 777 88 17 E-mail : info@ajan.ru
Классификация оборудования для резки кислородом
По способу обработки резка бывает ручная и механизированная. Существуют ручные резаки, работа которых характеризуется достаточно высокой точностьюю Они подразделяются на универсальные, специальные, для фигурного и прямого раскроя. При необходимости обработки больших объемов металла рационально использовать переносные аппараты «Гугарк», большие партии одинаковых изделий успешно вырезаются с помощью шарнирных машин АСШ-86. Промышленные предприятия чаще всего используют портально-консольные устройства.
Особенности рабочего процесса
Резка, как и другой рабочие процесс, требует внимательности и соблюдения техники безопасности:
При выполнении разделительной кислородной резки необходимо учитывать требования, предъявляемые к точности резки и качеству поверхности реза. Большое влияние на качество реза и производительность резки оказывает подготовка металла под резку. Перед началом резки листы подают на рабочее место и укладывают на подкладки так, чтобы обеспечить беспрепятственное удаление шлаков из зоны реза. Зазор между полом и нижним листом должен быть не менее 100-150 мм. Поверхность металла перед резкой должна быть очищена. На практике окалину, ржавчину, краску и другие загрязнения удаляют с поверхности металла нагревом зоны резки газовым пламенем с последующей зачисткой стальной щеткой. Вырезаемые детали размечают металлической линейкой, чертилкой и мелом. Часто разрезаемый лист подают к рабочему месту резчика уже размеченным.
Перед началом резки газорезчик должен установить необходимое давление газов на ацетиленовом и кислородном редукторах, подобрать нужные номера наружного и внутреннего мундштуков в зависимости от вида и толщины разрезаемого металла.
Процесс резки начинают с нагрева металла в начале реза до температуры воспламенения металла в кислороде. Затем пускают режущий кислород и перемещают резак по линии реза.
Для обеспечения высокого качества реза расстояние между мундштуком и поверхностью разрезаемого металла необходимо поддерживать постоянным. Для этой цели резаки комплектуются направляющими тележками. В зависимости от толщины разрезаемого металла расстояние между мундштуком и металлом составляет:
При работе на газах-заменителях ацетилена указанные расстояния между мундштуком и поверхностью разрезаемого металла увеличивают на 30-40%.
Основными параметрами режима кислородной резки являются: мощность подогревающего пламени, давление режущего кислорода и скорость резки. Мощность подогревающего пламени характеризуется расходом горючего газа в единицу времени и зависит от толщины разрезаемого металла. Она должна обеспечивать быстрый подогрев металла в начале резки до температуры воспламенения и необходимый нагрев его в процессе резки. Для резки металла толщиной до 300 мм применяют нормальное пламя. При резке металла больших толщин лучшие результаты получают при использовании пламени с избытком горючего. При этом длина видимого факела пламени должна быть больше толщины разрезаемого металла.
Читать также: Регулировка карбюратора бензопилы STIHL 660 своими руками
Выбор давления режущего кислорода зависит от толщины разрезаемого металла, размера режущего сопла и чистоты кислорода. При увеличении давления кислорода увеличивается его расход. Давление кислорода выбирается в зависимости от толщины металла:
Чем чище кислород, тем меньше его расход на 1 пог. м реза. Абсолютная величина давления кислорода зависит от конструкции резака и мундштуков, величин сопротивлений в кислородоподводящей арматуре и коммуникациях.
Скорость перемещения резака должна соответствовать скорости горения металла. От скорости резки зависят устойчивость процесса и качество вырезаемых разрезаемых кромок, а большая – к появлению не прорезанных до конца, участков реза. Скорость резки зависит от толщины и свойств участков реза. Скорость резки зависит от толщины и свойств разрезаемого металла. При резке сталей малых толщин (до 20 мм) скорость резки зависит от мощности подогревающего пламени. Например, при резке стали толщиной 5 мм около 35% тепла поступает от подогревающего пламени.
а – скорость резки мала, б – оптимальная скорость,
На скорость резки влияет также метод резки, форма линии реза и вид резки. Поэтому допустимые скорости резки определяют опытным путем в зависимости от толщины металла, вида и метода резки. При правильно выбранной скорости резки отстаивание линий реза не должно превышать 10-15% толщины разрезаемого металла.
Режимы ручной резки листового проката
На рис. 2 схематически показан характер выброса шлака. Если скорость кислородной резки мала, то наблюдается отклонение пучка искр в направлении резки (рис 1, а). При завышенной скорости резки отклонение пучка искр происходит в сторону, обратную направлению резки (рис. 1, б). Скорость перемещения резака считают нормальной, если пучок искр будет выходить почти параллельно кислородной струе (рис. 1, в). Режимы ручной резки листового проката приведены в табл. 1.
Ширина и чистота реза зависят от способа резки. Машинная резка дает более чистые кромки и меньшую ширину реза, чем ручная. Чем больше толщина разрезаемого металла, тем больше шероховатость кромок и ширина реза. В зависимости от толщины металла ориентировочная ширина реза составляет:
В начале резки мундштук располагают перпендикулярно поверхности металла или с небольшим наклоном (5-10 єC) в сторону, обратную направлению резки. По мере углубления в массу металла ослабевает действие подогревающего пламени, уменьшается скорость кислородной струи, поэтому при резке происходит отстаивание режущей струи Отстаивание увеличивается с увеличением скорости резки, отстаивание можно компенсировать наклоном мундштука вперед по направлению движения.
На качество резки большое влияние оказывает чистота режущего кислорода. Для резки применяют кислород с чистотой не менее 98,5 % по объему. Снижение чистоты кислорода приводит к снижению скорости резки (табл. 8), увеличению расхода кислорода, снижению чистоты кромок, значительному количеству грата.
Основные параметры режима кислородной резки: давление кислорода, расход режущего кислорода, мощность подогревающего пламени и скорость резки.
При увеличении давления кислорода увеличивают и скорость резки, сохраняя качество поверхности реза. Однако для каждого сопла и толщины металла существует оптимальное давление, при повышении которого допустимая скорость резки уменьшается, удельный расход кислорода на единицу длины резки увеличивается, а качество резки ухудшается. Параметры резки подбираются по специальным таблицам.